Body awareness mediates the relationship between body mass index and lipid profiles in adolescents
- PMID: 35673458
- PMCID: PMC9167376
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-022-01021-3
Body awareness mediates the relationship between body mass index and lipid profiles in adolescents
Abstract
Aim: The purposes of this study were to 1) investigate the relationship between body awareness and anthropometric measurements and lipid profile in adolescents, 2) determine the potential mediating effect of body awareness due to body mass index (BMI) on lipid profiles.
Materials and methods: The study was carried out with 272 volunteer adolescents between the ages of 10-18 who applied to a private nutrition and counseling clinic. Anthropometric measurements of the participants were evaluated including body height body weight, waist and neck, and mid-upper arm circumference. The lipid profile including total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-c), low density lipoprotein-cholestero (LDL-c) and triglyceride was analyzed. A body awareness questionnaire (BAQ), a seven-point Likert-type questionnaire consisting of 18 statements, was administered and questionnaire is interpreted on the total score, and the higher score reflects better body sensitivity. Correlation analysis, linear regression analysis, and path analysis were performed.
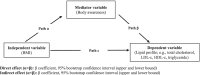
Results: Body awareness scores were negatively associated with all anthropometric measurements, namely, BMI, body weight and fat percentage waist and neck and mid-upper arm circumference (all p < 0.05). Body awareness was found to have a negative linear regression relationship with lipid profiles except than HDL-c. The results of path analysis showed that the direct effect of lipid profiles in relation to BMI and the indirect effect of BAQ was statistically significant. This result indicates that body awareness partial mediated the relationship between BMI and lipid profiles.
Conclusion: The research results suggested that increased body awareness is associated body awareness with a lower risk and a decreased body awareness is associated with a higher risk of developing obesity and dyslipidemia.
Keywords: Adolescents; Body awareness; Dyslipidemia; Lipid profile; Obesity.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors declare that there is no confict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chestnov O. World Health Organization global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases. Geneva, Switzerland; 2013.
-
- Arellano-Ruiz P, García-Hermoso A, García-Prieto JC, Sánchez-López M, Martínez Vizcaíno V, Solera-Martínez M. Predictive ability of waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio for cardiometabolic risk screening among Spanish children. Nutrients. 2020;12:415–426. doi: 10.3390/nu12020415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

