Atypical and aggressive diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor in a young adult: A case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 35673647
- PMCID: PMC9168386
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_1255_2021
Atypical and aggressive diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor in a young adult: A case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: DLGNT is a rare tumor, commonly diagnosed in pediatric age; in most cases, the pathology presents a slow and indolent evolution. We present a case report of a young adult affected by DLGNT characterized by aggressive and atypical behavior.
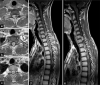
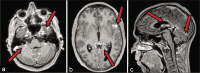
Case description: A 21-year-old male presented with mild paraparesis and hypoesthesia with a D2 level. MRI scan of the brain and spine showed a dorsal intramedullary lesion; a diffuse craniospinal leptomeningeal thickening was also present. After a week, the neurological status deteriorated rapidly with paraparesis worsening and onset of acute hydrocephalus. The patient underwent external ventricular drain positioning; a C7-D4 laminectomy was subsequently performed with partial tumor resection. Histological examination revealed a DLGNT with aggressive aspects (Ki67 30%). Postoperatively, the patient showed an immediate mild worsening of the lower limbs deficit. After a few days, severe further neurological deterioration occurred with progressive motor deficit to the upper limbs and ultimately respiratory failure. Mechanical ventilation was necessary and the patient was transferred to the ICU; during the following weeks, he developed tetraplegia and underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt positioning. By the time, the histological diagnosis was available, the clinical status would not allow radiotherapy or chemotherapy. The patient deceased approximately 90 days after hospitalization due to respiratory complications.
Conclusion: DLGNT is a rare tumor; diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion and confirmation with biopsy. Although most cases have an indolent course, some patients may have aggressive forms. High proliferation index, hydrocephalus occurrence, and massive craniospinal leptomeningeal spread appear to be associated with worse prognosis.
Keywords: Brain tumor; Central nervous system tumor; DLGNT; Diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor; Spine tumor.
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abongwa C, Cotter J, Tamrazi B, Dhall G, Davidson T, Margol A. Primary diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumors of the central nervous system: Report of three cases and review of literature. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2020;37:248–58. - PubMed
-
- Agamanolis DP, Katsetos CD, Klonk CJ, Bartkowski HM, Ganapathy S, Staugaitis SM, et al. An unusual form of superficially disseminated glioma in children: report of 3 cases. J Child Neurol. 2012;27:727–33. - PubMed
-
- Aguilera D, Castellino RC, Janss A, Schniederjan M, McNall R, MacDonald T, et al. Clinical responses of patients with diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumors to chemotherapy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018;34:329–34. - PubMed
-
- Cho HJ, Myung JK, Kim H, Park CK, Kim SK, Chung CK, et al. Primary diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2015;32:49–55. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
