Novel concepts in psoriasis: histopathology and markers related to modern treatment approaches
- PMID: 35673809
- PMCID: PMC9289716
- DOI: 10.47162/RJME.62.4.02
Novel concepts in psoriasis: histopathology and markers related to modern treatment approaches
Abstract
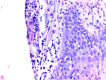
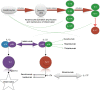
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting over 2% of the worldwide population. From an anatomopathological point of view, psoriasis is characterized by immune cells infiltration, epidermal hyperproliferation, and abnormal keratinocyte differentiation. Understanding the pathogenesis of psoriasis will allow clinicians to manage this complex disease. Under these conditions, the application of effective treatments requires a thorough knowledge of all the pathogenetic mechanisms that lead to psoriasis. Numerous immunopathological pathways play crucial roles in the development of new therapies, such as biological therapies, which have been a breakthrough in psoriasis's treatment. Pharmacogenetics is an essential factor in the patient's response to treatment. One important pathway targeted by modern treatments is the interleukin (IL)-23∕T-helper (Th)17 axis. Like IL-17 inhibitors, IL-23 blockers are a very effective therapy for this autoimmune disease. It is considered that micro-ribonucleic acids (microRNAs) are the starting point for any autoimmune disease. Studying certain microRNA (miR) involved in the inflammatory pathway in psoriasis can find direct targets to future treatments that can even be more specific than actual biological therapies. As such, miR-210 has proven to be up-regulated in psoriasis, also leading to the up-regulation of the Th1∕Th17 axis. On the other hand, miR-187 was found to be down-regulated, influencing the outcome of psoriasis by increasing the proliferation of IL-6 stimulated keratinocytes and consecutively generating epidermal thickening. In this review, we are aiming to do an up-to-date briefing of psoriasis histopathology and pharmacogenetic factors that are considered for the accurate evaluation of treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MiR-330 inhibits IL-22-induced keratinocyte proliferation through targeting CTNNB1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:803-811. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28501007
-
MiR-20a-3p regulates TGF-β1/Survivin pathway to affect keratinocytes proliferation and apoptosis by targeting SFMBT1 in vitro.Cell Signal. 2018 Sep;49:95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29886071
-
Downregulated miR-187 contributes to the keratinocytes hyperproliferation in psoriasis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):3661-3674. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27135. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30607907
-
Psoriasis and other Th17-mediated skin diseases.J UOEH. 2010 Dec 1;32(4):317-28. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.32.317. J UOEH. 2010. PMID: 21226422 Review.
-
Review: A Contemporary, Multifaced Insight into Psoriasis Pathogenesis.J Pers Med. 2024 May 16;14(5):535. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050535. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psoriasis: What Is New in Markers of Disease Severity?Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Feb 18;60(2):337. doi: 10.3390/medicina60020337. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38399624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Common Genetic Background for Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 13;8(8):e71128. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71128. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40809699 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Treatment for the Management of Mild-to-Moderate Psoriasis: A Critical Appraisal of the Current Literature.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Nov;13(11):2527-2547. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01024-9. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37737941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xiaoyin-anshen formula alleviates psoriasis complicated by sleep disturbances by regulating melatonin, antioxidant enzymes, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 1;15:1427985. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1427985. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39411067 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed-dose combination of calcipotriene/betamethasone dipropionate foam for the management of mild-to-moderate psoriasis in daily clinical practice: a collection of clinical experiences.Drugs Context. 2024 Oct 9;13:2023-11-5. doi: 10.7573/dic.2023-11-5. eCollection 2024. Drugs Context. 2024. PMID: 39416771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raychaudhuri SP, Farber EM. The prevalence of psoriasis in the world. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15(1):16–17. - PubMed
-
- Christophers E. Psoriasis - epidemiology and clinical spectrum. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26(4):314–320. - PubMed
-
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(3):512–516. - PubMed
-
- Burgdorf WHC, Plewig G, Wolff HH, Landthaler M, editors. Braun-Falco’s Dermatology. 3. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2009. pp. 506–527.https://link.springer.com/book/9783540293125
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

