Analysis of outer hair cell electromechanics reveals power delivery at the upper-frequency limits of hearing
- PMID: 35673856
- PMCID: PMC9174718
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0139
Analysis of outer hair cell electromechanics reveals power delivery at the upper-frequency limits of hearing
Abstract
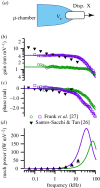
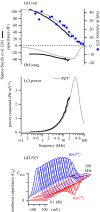
Outer hair cells are the cellular motors in the mammalian inner ear responsible for sensitive high-frequency hearing. Motor function over the frequency range of human hearing requires expression of the protein prestin in the OHC lateral membrane, which imparts piezoelectric properties to the cell membrane. In the present report, electrical power consumption and mechanical power output of the OHC membrane-motor complex are determined using previously published voltage-clamp data from isolated OHCs and membrane patches. Results reveal that power output peaks at a best frequency much higher than implied by the low-pass character of nonlinear capacitance, and much higher than the whole-cell resistive-capacitive corner frequency. High frequency power output is enabled by a -90° shift in the phase of electrical charge displacement in the membrane, manifested electrically as emergence of imaginary-valued nonlinear capacitance.
Keywords: biological motor; cochlea; electromotility; imaginary capacitance; piezoelectricity; prestin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Megahertz Sampling of Prestin (SLC26a5) Voltage-Sensor Charge Movements in Outer Hair Cell Membranes Reveals Ultrasonic Activity that May Support Electromotility and Cochlear Amplification.J Neurosci. 2023 Apr 5;43(14):2460-2468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2033-22.2023. Epub 2023 Mar 3. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36868859 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Outer-Hair-Cell RC Time Constant: A Feature, Not a Bug, of the Mammalian Cochlea.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2023 Apr;24(2):129-145. doi: 10.1007/s10162-022-00884-w. Epub 2023 Feb 1. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36725778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cochlear outer hair cell speed paradox.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):21880-21888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2003838117. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32848062 Free PMC article.
-
Outer hair cell electromotility is low-pass filtered relative to the molecular conformational changes that produce nonlinear capacitance.J Gen Physiol. 2019 Dec 2;151(12):1369-1385. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201812280. Epub 2019 Nov 1. J Gen Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31676485 Free PMC article.
-
Prestin and electromotility may serve multiple roles in cochlear outer hair cells.Hear Res. 2022 Sep 15;423:108428. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2021.108428. Epub 2021 Dec 26. Hear Res. 2022. PMID: 34987016 Review.
Cited by
-
Megahertz Sampling of Prestin (SLC26a5) Voltage-Sensor Charge Movements in Outer Hair Cell Membranes Reveals Ultrasonic Activity that May Support Electromotility and Cochlear Amplification.J Neurosci. 2023 Apr 5;43(14):2460-2468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2033-22.2023. Epub 2023 Mar 3. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36868859 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Outer-Hair-Cell RC Time Constant: A Feature, Not a Bug, of the Mammalian Cochlea.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2023 Apr;24(2):129-145. doi: 10.1007/s10162-022-00884-w. Epub 2023 Feb 1. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36725778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A parametric blueprint for optimum cochlear outer hair cell design.J R Soc Interface. 2023 Feb;20(199):20220762. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0762. Epub 2023 Feb 15. J R Soc Interface. 2023. PMID: 36789510 Free PMC article.
-
Sound-evoked tonic motility of cochlear outer hair cells in mice with stereociliary defects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 29;122(30):e2505176122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2505176122. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40694329
-
Chloride binding does not influence prestin motor speed at very high frequencies in the mouse outer hair cell.Structure. 2025 Aug 7;33(8):1417-1424.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2025.04.019. Epub 2025 May 21. Structure. 2025. PMID: 40403717
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

