Determinants of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I among Radial Head Fracture Patients with Unilateral Arthroplasty
- PMID: 35673902
- PMCID: PMC9251304
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13320
Determinants of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I among Radial Head Fracture Patients with Unilateral Arthroplasty
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to assess the proportions of complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I) in radial head fracture patients undergoing unilateral arthroplasty and to explore associated factors.
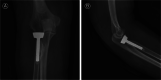
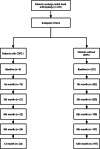
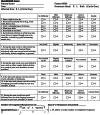
Methods: This is a prospective observational study. From March 2016 to May 2019, a total of 221 adult patients with radial head fracture patients were included in consecutive studies and completed the 1-year follow-up. All patients were treated by unilateral arthroplasty. At each follow-up visit, the visual analogue scale was used to measure patients' pain level. Occurrence of CRPS I, which was diagnosed by Budapest criteria, was the main outcome collected at baseline and the 1-, 3-, 6-, and 9-month follow-ups. The baseline data were collected before surgery and included demographic and clinical data. Independent t-tests and χ2 tests were used as univariate analyses to compare the baseline data of patients with and without CRPS I. Multivariate analysis (Backword-Wald) was used to identify factors independently associated with CRPS I.
Results: The proportion of CRPS I cases among radial head fracture patients undergoing unilateral arthroplasty was 11% (n = 24). A total of 19 (79%) patients were diagnosed with CRPS I within 1 month after surgery. Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that female gender (odds ratios [OR]: 1.537; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.138-2.072), age younger than 60 years (OR: 1.682; 95% CI: 1.246-2.267), moderate and severe Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS) pain (OR: 3.229; 95% CI: 2.392-4.351) and anxiety (OR: 83.346; 95% CI: 61.752-112.320) were independently associated with CRPS I.
Conclusions: This exploratory study reported that the incidence of CRPS I developing after radial head arthroplasty was 11%. Female sex, younger age, moderate and severe MEPS pain and anxiety patients seems more likely to develop CRPS I.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Complex regional pain syndromes; Fractures; Logistic models; Radial heads.
© 2022 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Ha AS, Petscavage JM, Chew FS. Radial head arthroplasty: a radiologic outcome study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(5):1078–82. - PubMed
-
- Madsen JE, Flugsrud G. Radial head fractures: indications and technique for primary arthroplasty. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2008;34(2):105–12. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz MR, Murtha AS, Clohisy JC, Group AS . Developmental dysplasia of the hip in adolescents and young adults. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(3):91–101. - PubMed
-
- de Mos M. , de Bruijn AGJ, Huygen FJPM, Dieleman JP, Stricker BH, Sturkenboom MC. The incidence of complex regional pain syndrome: a population‐based study. Pain, 2007, 129(1–2):12–20. - PubMed
-
- Sandroni P, Benrud‐Larson LM, McClelland RL, Low PA. Complex regional pain syndrome type I: incidence and prevalence in Olmsted county, a population‐based study. Pain. 2003;103(1–2):199–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

