[ALDH3B1 expression is correlated with histopathology and long-term prognosis of gastric cancer]
- PMID: 35673905
- PMCID: PMC9178630
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.05.02
[ALDH3B1 expression is correlated with histopathology and long-term prognosis of gastric cancer]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 3B1 (ALDH3B1) in gastric cancer and explore its correlation with the pathological parameters and long-term prognosis of the patients.
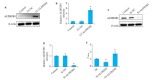
Methods: We analyzed the clinical data of 101 patients who underwent radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer in our hospital between January, 2013 and November, 2016, and examined the expression of ALDH3B1 in paraffin-embedded samples of gastric cancer tissues and adjacent tissues from these cases by immunohistochemical staining. We evaluated the correlation between ALDH3B1 expressions and histopathological parameters and assessed the predictive value of ALDH3B1 expression for long-term survival of the patients. We also examined the effect of lentivirus-mediated interference and overexpression of ALDH3B1 on the malignant behaviors of MGC-803 gastric cancer cells.
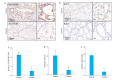
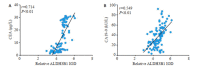
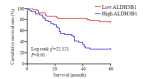
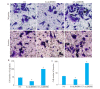
Results: The expressions of ALDH3B1 and Ki67 were significantly higher in gastric cancer tissues than in adjacent tissues (P < 0.05). In gastric cancer patients, ALDH3B1 expression was positively correlated with peripheral blood CEA and CA19-9 levels (P < 0.01). The proportion of patients with CEA ≥5 μg/L, CA19-9 ≥37 kU/L, T stage of 3- 4, and N stage of 2-3 was significantly greater in high ALDH3B1 expression group than in low expression group. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the 5-year survival rate was significantly lower in gastric cancer patients with high ALDH3B1 expressions (P < 0.01). Univariate and Cox multiple regression analyses identified a high expression of ALDH3B1 (P < 0.05, HR= 0.231, 95% CI: 0.064-0.826), CEA≥5 μg/L (P < 0.01, HR=4.478, 95% CI: 1.530-13.110), CA19-9≥37 kU/L (P < 0.01, HR=3.877, 95% CI: 1.625-9.247), T stage of 3-4 (P < 0.01, HR=4.953, 95% CI: 1.768-13.880), and N stage of 2-3 (P < 0.05, HR=2.152, 95% CI: 1.152-4.022) as independent risk factors affecting 5-year survival after radical gastrectomy. The relative ALDH3B1 expression level, at the cut-off point of 4.66, showed a sensitivity of 76.47% and a specificity of 76% for predicting 5-year postoperative death (P < 0.01). In the cell experiment, overexpression of ALDH3B1 obviously promoted the proliferation, migration and invasion of MGC-803 cells.
Conclusion: As an independent risk factor affecting 5-year survival after radical gastrectomy, ALDH3B1 is highly expressed in gastric cancer and correlated with pathological parameters of the tumor, and a high ALDH3B1 expression may promote proliferation, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells.
目的: 探究乙醛脱氢酶3B1(ALDH3B1)在胃癌组织中的表达情况,明确其与胃癌病理参数和远期预后的关系。
方法: 纳入分析我院行胃癌根治术患者101例,治疗时间范围在2013年1月~2016年11月,采用免疫组织化学法检测胃癌和癌旁组织中ALDH3B1的表达,统计学分析ALDH3B1与病理组织学参数的关系以及对胃癌术后远期生存的预测评估价值;对MGC-803胃癌细胞系采用慢病毒特异性干扰和过表达ALDH3B1,经免疫印迹法验证基因调控效果,实验分为正常对照组(NC),干扰组(Si-ALDH3B1)和过表达组(LV-ALDH3B1),探究ALDH3B1作用于胃癌细胞恶性行为的影响。
结果: 胃癌组织中ALDH3B1和Ki67的表达显著增加(P < 0.05);胃癌组织中ALDH3B1表达量与外周血CEA及CA19-9间均存在正相关关系(P < 0.01)。ALDH3B1高表达组患者CEA≥5 μg/L、CA19-9≥37 kU/L、T分期为3~4期及N分期为2~3期的比例显著高于ALDH3B1低表达组(P < 0.05)。K-M生存分析结果显示ALDH3B1高表达组患者5年生存率显著降低(P < 0.01)。经单因素及Cox多元回归模型分析得出ALDH3B1高表达(P < 0.05,HR=0.231,95% CI:0.064~0.826)、CEA≥5 μg/L(P < 0.01,HR=4.478,95% CI:1.530~ 13.110)、CA19-9≥37 kU/L(P < 0.01,HR=3.877,95% CI:1.625~9.247)、T分期为3~4期(P < 0.01,HR=4.953,95% CI:1.768~ 13.880)及N分期为2~3期(P < 0.05,HR=2.152,95% CI:1.152~4.022)为影响胃癌根治术后5年生存期的独立危险因素。此外,以ALDH3B1相对表达量4.66为截点值,预判术后5年死亡的敏感性为76.47%,特异性为76%(P < 0.01);细胞学实验证明ALDH3B1高表达可促进胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移及侵袭能力。
结论: ALDH3B1在胃癌组织中高表达与肿瘤病理学参数相关,是胃癌根治术后5年生存率的独立危险因素,可能促进肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭及转移等生物学过程。
Keywords: aldehyde dehydrogenase 3B1; gastric cancer; pathology; risk factor analysis; survival analysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Prognostic Value of the Expression of Myeloid Leukemia Factor 1-Interacting Protein in Gastric Cancer and Its Regulatory Role in Tumor Progression].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Jan;54(1):114-121. doi: 10.12182/20230160103. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 36647653 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Association of adenylate cyclase-associated protein 2 expression with histopathology and long-term prognosis of gastric cancer].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Sep 30;39(9):1052-1058. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.09.08. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31640951 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Clinical significance of prognostic nutritional index in patients with advanced gastric cancer].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 25;21(2):180-184. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29492917 Chinese.
-
Comparison of CEA and CA19-9 as a predictive factor for recurrence after curative gastrectomy in gastric cancer.BMC Surg. 2022 Jun 3;22(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01667-z. BMC Surg. 2022. PMID: 35655198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consideration of tumor size improves the accuracy of TNM predictions in patients with gastric cancer after curative gastrectomy.Surg Oncol. 2013 Sep;22(3):167-71. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Surg Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23787074 Review.
Cited by
-
[High expression of death-associated protein 5 promotes glucose metabolism in gastric cancer cells and correlates with poor survival outcomes].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Jul 20;43(7):1063-1070. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.07.02. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37488788 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[High expression of MRPL13 promotes cell cycle progression and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 signaling to affect long-term prognosis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Sep 20;43(9):1558-1566. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.09.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37814870 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–53. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31937. [Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144(8): 1941-53.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, et al. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):4012. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114012. [Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, et al. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(11): 4012.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wong MCS, Huang JJ, Chan PSF, et al. Global incidence and mortality of gastric cancer, 1980-2018. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):e2118457. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18457. [Wong MCS, Huang JJ, Chan PSF, et al. Global incidence and mortality of gastric cancer, 1980-2018[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(7): e2118457.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
