Intestinal Gastrin/CCKBR (Cholecystokinin B Receptor) Ameliorates Salt-Sensitive Hypertension by Inhibiting Intestinal Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Activity Through a PKC (Protein Kinase C)-Mediated NHERF1 and NHERF2 Pathway
- PMID: 35674015
- PMCID: PMC9278716
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18791
Intestinal Gastrin/CCKBR (Cholecystokinin B Receptor) Ameliorates Salt-Sensitive Hypertension by Inhibiting Intestinal Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Activity Through a PKC (Protein Kinase C)-Mediated NHERF1 and NHERF2 Pathway
Abstract
Background: The present study directly tested the crucial role of intestinal gastrin/CCKBR (cholecystokinin B receptor) in the treatment of salt-sensitive hypertension.
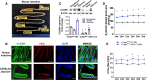
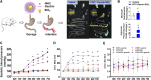
Methods: Adult intestine-specific Cckbr-knockout mice (Cckbrfl/fl villin-Cre) and Dahl salt-sensitive rats were studied on the effect of high salt intake (8% NaCl, 6-7 weeks) on intestinal Na+/H+ exchanger 3 expression, urine sodium concentration, and blood pressure. High-salt diet increased urine sodium concentration and systolic blood pressure to a greater extent in Cckbrfl/fl villin-Cre mice and Dahl salt-sensitive rats than their respective controls, Cckbrfl/fl villin mice and SS13BN rats. We constructed gastrin-SiO2 microspheres to enable gastrin to stimulate specifically and selectively intestinal CCKBR without its absorption into the circulation.
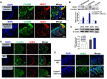
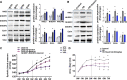
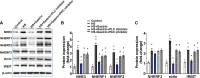
Results: Gastrin-SiO2 microspheres treatment prevented the high salt-induced hypertension and increase in urine Na concentration by inhibiting intestinal Na+/H+ exchanger 3 trafficking and activity, increasing stool sodium without inducing diarrhea. Gastrin-mediated inhibition of intestinal Na+/H+ exchanger 3 activity, related to a PKC (protein kinase C)-mediated activation of NHERF1 and NHERF2.
Conclusions: These results support a crucial role of intestinal gastrin/CCKBR in decreasing intestinal sodium absorption and keeping the blood pressure in the normal range. The gastrointestinal administration of gastrin-SiO2 microspheres is a promising and safe strategy to treat salt-sensitive hypertension without side effects.
Keywords: blood pressure; cholecystokinin; gastrins; intestines; sodium.
Figures
References
-
- Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2012. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC, Moran J, Forsblom C, Harjutsalo V, Thorn L, Ahola A, Wadén J, Tolonen N, Saraheimo M, Gordin D, et al. ; FinnDiane Study Group. The association between dietary sodium intake, ESRD, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:861–866. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1722 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D, Singh GM, Powles J. Sodium and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2138–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1412113 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

