Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals the Tissue Architecture in Human High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 35675036
- PMCID: PMC9662915
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0296
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals the Tissue Architecture in Human High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The heterogeneity of high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) is not well studied, which severely hinders clinical treatment of HGSOC. Thus, it is necessary to characterize the heterogeneity of HGSOC within its tumor microenvironment (TME).
Experimental design: The tumors of 7 treatment-naïve patients with HGSOC at early or late stages and five age-matched nonmalignant ovarian samples were analyzed by deep single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq).
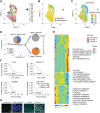
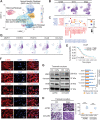
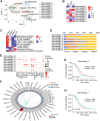
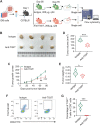
Results: A total of 59,324 single cells obtained from HGSOC and nonmalignant ovarian tissues were sequenced by scRNA-seq. Among those cells, tumor cells were characterized by a set of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated gene signatures, in which a combination of NOTCH1, SNAI2, TGFBR1, and WNT11 was further selected as a genetic panel to predict the poor outcomes of patients with HGSOC. Matrix cancer-associated fibroblasts (mCAF) expressing α-SMA, vimentin, COL3A, COL10A, and MMP11 were the dominant CAFs in HGSOC tumors and could induce EMT properties of ovarian cancer cells in the coculture system. Specific immune cell subsets such as C7-APOBEC3A M1 macrophages, CD8+ TRM, and TEX cells were preferentially enriched in early-stage tumors. In addition, an immune coinhibitory receptor TIGIT was highly expressed on CD8+ TEX cells and TIGIT blockade could significantly reduce ovarian cancer tumor growth in mouse models.
Conclusions: Our transcriptomic results analyzed by scRNA-seq delineate an ecosystemic landscape of HGSOC at early or late stages with a focus on its heterogeneity with TME. The major applications of our findings are a four-EMT gene model for prediction of HGSOC patient outcomes, mCAFs' capability of enhancing ovarian cancer cell invasion and potential therapeutic value of anti-TIGIT treatment.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Seidman JD, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Haiba M, Boice CR, Kurman RJ, Ronnett BM. The histologic type and stage distribution of ovarian carcinomas of surface epithelial origin. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:41–4. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin LA, Huang B, Miller RW, Tucker T, Goodrich ST, Podzielinski I, et al. . Ten-year relative survival for epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol 2012;120:612–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

