Curation of the AMRFinderPlus databases: applications, functionality and impact
- PMID: 35675101
- PMCID: PMC9455714
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000832
Curation of the AMRFinderPlus databases: applications, functionality and impact
Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a significant public health threat. Low-cost whole-genome sequencing, which is often used in surveillance programmes, provides an opportunity to assess AMR gene content in these genomes using in silico approaches. A variety of bioinformatic tools have been developed to identify these genomic elements. Most of those tools rely on reference databases of nucleotide or protein sequences and collections of models and rules for analysis. While the tools are critical for the identification of AMR genes, the databases themselves also provide significant utility for researchers, for applications ranging from sequence analysis to information about AMR phenotypes. Additionally, these databases can be evaluated by domain experts and others to ensure their accuracy. Here we describe how we curate the genes, point mutations and blast rules, and hidden Markov models used in NCBI's AMRFinderPlus, along with the quality-control steps we take to ensure database quality. We also describe the web interfaces that display the full structure of the database and their newly developed cross-browser relationships. Then, using the Reference Gene Catalog as an example, we detail how the databases, rules and models are made publicly available, as well as how to access the software. In addition, as part of the Pathogen Detection system, we have analysed over 1 million publicly available genomes using AMRFinderPlus and its databases. We discuss how the computed analyses generated by those tools can be accessed through a web interface. Finally, we conclude with NCBI's plans to make these databases accessible over the long-term.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; curation; genomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
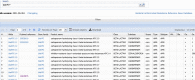

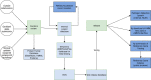

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

