Digenic Alport Syndrome
- PMID: 35675912
- PMCID: PMC9718039
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03120322
Digenic Alport Syndrome
Erratum in
-
Correction: Digenic Alport Syndrome.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Apr 1;18(4):511. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000096. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37026752 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
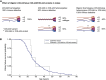
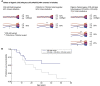
Digenic Alport syndrome refers to the inheritance of pathogenic variants in COL4A5 plus COL4A3 or COL4A4 or in COL4A3 plus COL4A4 Where digenic Alport syndrome includes a pathogenic COL4A5 variant, the consequences depend on the sex of the affected individual, COL4A5 variant "severity," and the nature of the COL4A3 or COL4A4 change. A man with a pathogenic COL4A5 variant has all his collagen IV α3α4α5-heterotrimers affected, and an additional COL4A3 or COL4A4 variant may not worsen disease. A woman with a pathogenic COL4A5 variant has on average 50% of her heterotrimers affected, which is increased to 75% with a further COL4A3 or COL4A4 variant and associated with a higher risk of proteinuria. In digenic Alport syndrome with pathogenic COL4A3 and COL4A4 variants, 75% of the heterotrimers are affected. The COL4A3 and COL4A4 genes occur head-to-head on chromosome 2, and inheritance is autosomal dominant when both variants affect the same chromosome (in cis) or recessive when they affect different chromosomes (in trans). This form of digenic disease results in increased proteinuria and a median age of kidney failure intermediate between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. Previous guidelines have suggested that all pathogenic or likely pathogenic digenic variants should be identified and reported. Affected family members should be identified, treated, and discouraged from kidney donation. Inheritance within a family is easier to predict if the two variants are considered independently and if COL4A3 and COL4A4 variants are known to be inherited on the same or different chromosomes.
Keywords: Alport syndrome; COL4A3; COL4A4; COL4A5 genes; collagen; digenic Alport syndrome; genetic renal disease; kidney failure; proteinuria.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of heterozygous pathogenic COL4A3 or COL4A4 variants on patients with X-linked Alport syndrome.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 May;7(5):e647. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.647. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 30883042 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Digenic Disease in a Caucasian Family with COL4A3 and COL4A5 Mutations.Nephron. 2019;141(3):213-218. doi: 10.1159/000495764. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Nephron. 2019. PMID: 30661074
-
Lithuanian Study on COL4A3 and COL4A4 Genetic Variants in Alport Syndrome: Clinical Characterization of 52 Individuals from 38 Families.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 7;26(15):7639. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157639. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806767 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Variants in the Genes Affected in Alport Syndrome (COL4A3-COL4A5) and Their Association With Other Kidney Conditions: A Review.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Dec;78(6):857-864. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.04.017. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 34245817 Review.
-
Heterozygous Pathogenic COL4A3 and COL4A4 Variants (Autosomal Dominant Alport Syndrome) Are Common, and Not Typically Associated With End-Stage Kidney Failure, Hearing Loss, or Ocular Abnormalities.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Jun 7;7(9):1933-1938. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.06.001. eCollection 2022 Sep. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 36090501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal mRNA Splicing Effect of COL4A3 to COL4A5 Unclassified Variants.Kidney Int Rep. 2023 Apr 10;8(7):1399-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.04.001. eCollection 2023 Jul. Kidney Int Rep. 2023. PMID: 37441478 Free PMC article.
-
Reclassification of Genetic Testing Results: A Case Report Demonstrating the Need for Structured Re-Evaluation of Genetic Findings.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2024 Apr 14;11:20543581241242562. doi: 10.1177/20543581241242562. eCollection 2024. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38623282 Free PMC article.
-
Alport Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2023 Oct 16;15(10):e47129. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47129. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case report: Alport syndrome and growth hormone deficiency associated with a new COL4A4 mutation.Transl Pediatr. 2024 May 31;13(5):847-855. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-569. Epub 2024 May 17. Transl Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38840691 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Collagen IV nephropathies: Alport syndrome and beyond.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 30;9:1039949. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1039949. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36250080 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gibson J, Fieldhouse R, Chan MMY, Sadeghi-Alavijeh O, Burnett L, Izzi V, Persikov AV, Gale DP, Storey H, Savige J; Genomics England Research Consortium : Prevalence estimates of predicted pathogenic COL4A3-COL4A5 variants in a population sequencing database and their implications for Alport syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 32: 2273–2290, 2021. 10.1681/ASN.2020071065 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kashtan CE, Ding J, Garosi G, Heidet L, Massella L, Nakanishi K, Nozu K, Renieri A, Rheault M, Wang F, Gross O: Alport syndrome: A unified classification of genetic disorders of collagen IV α345: A position paper of the Alport Syndrome Classification Working Group. Kidney Int 93: 1045–1051, 2018. 10.1016/j.kint.2017.12.018 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

