Roles of exosomal circRNAs in tumour immunity and cancer progression
- PMID: 35676257
- PMCID: PMC9177590
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04949-9
Roles of exosomal circRNAs in tumour immunity and cancer progression
Abstract
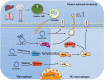
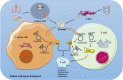
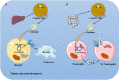
Tumour immunity plays an important role in the development of cancer. Tumour immunotherapy is an important component of antitumour therapy. Exosomes, a type of extracellular vesicle, act as mediators of intercellular communication and molecular transfer and play an essential role in tumour immunity. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a new type of noncoding RNA that are enriched within exosomes. In this review, we describe the effects of exosomal circRNAs on various immune cells and the mechanisms of these effects, including macrophages, neutrophils, T cells, and Natural killer (NK) cells. Next, we elaborate on the latest progress of exosome extraction. In addition, the function of exosomal circRNAs as a potential prognostic and drug sensitivity marker is described. We present the great promise of exosomal circRNAs in regulating tumour immunity, predicting patient outcomes, and evaluating drug efficacy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel insights into exosomal circular RNAs: Redefining intercellular communication in cancer biology.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Dec;11(12):e636. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.636. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34898043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GC-derived exosomal circMAN1A2 promotes cancer progression and suppresses T-cell antitumour immunity by inhibiting FBXW11-mediated SFPQ degradation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 25;44(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03288-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39856764 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal circRNAs: A new star in cancer.Life Sci. 2021 Mar 15;269:119039. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119039. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33454367 Review.
-
Presence and prospects of exosomal circRNAs in cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2023 Apr;62(4):47. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5495. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36866755 Review.
-
New insights into the potential of exosomal circular RNAs in mediating cancer chemotherapy resistance and their clinical applications.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Aug;177:117027. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117027. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38925018 Review.
Cited by
-
Colorectal cancer-secreted exosomal circ_001422 plays a role in regulating KDR expression and activating mTOR signaling in endothelial cells by targeting miR-195-5p.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):12227-12240. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05095-1. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37432457 Free PMC article.
-
Hijacking host extracellular vesicle machinery by hepatotropic viruses: current understandings and future prospects.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Oct 5;31(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01063-0. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 39369194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific Circular RNA Signature of Endothelial Cells: Potential Implications in Vascular Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 4;25(1):680. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010680. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203852 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-delivered circRPS5 inhibits the progression of melanoma via regulating the miR-151a/NPTX1 axis.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 29;18(6):e0287347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287347. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37384727 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Delivery Vehicles for Non-Coding RNAs: Potential Biomarkers for Chronic Liver Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 26;14(3):277. doi: 10.3390/biom14030277. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

