Optimizing and Evaluating the Transdermal Permeation of Hydrocortisone Transfersomes Formulation Based on Digital Analysis of the In Vitro Drug Release and Ex Vivo Studies
- PMID: 35676851
- PMCID: PMC10186384
- DOI: 10.2174/2667387816666220608115605
Optimizing and Evaluating the Transdermal Permeation of Hydrocortisone Transfersomes Formulation Based on Digital Analysis of the In Vitro Drug Release and Ex Vivo Studies
Abstract
Background: Transfersomes can be used to enhance transdermal drug delivery due to their flexibility and ability to incorporate various molecules. For example, hydrocortisone (HC), a corticosteroid, is taken by different routes and serves as immunosuppressive, anticancer, and antiallergenic; however, it is poorly absorbed by the skin.
Objective: Therefore, the current study suggested HC-loaded transfersomes as an alternative route of administration for reaching deeper skin layers or systemic circulation, to reduce the side effects of HC and improve its bioavailability.
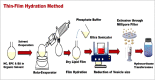
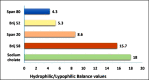
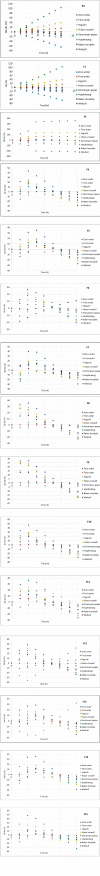
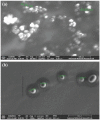
Methods: HC transfersomes were prepared by the thin-film hydration method and characterized for their vesicular size, zeta potential, drug entrapment efficiency, elasticity, FTIR spectroscopy, in vitro drug release, ex vivo permeation, and irritancy in rabbits. The optimized formulation, F15 (containing HC 20 mg, egg phosphatidylcholine (EPC) 400 mg, and 75 mg of Span 80), was chosen because it showed the highest (p< 0.05) EE% (60.4±0.80) and optimized sustained in vitro drug release (Q8 = 87.9±0.6%).
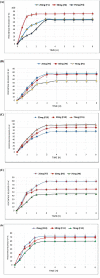
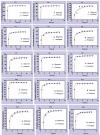
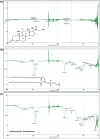
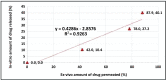
Results: Extensive analysis of the drug release data from all formulas was performed using the DDSolver software which quantitatively confirmed the successful formulation. The Weibull equation was the best model to fit the release data compared to others, and the release mechanism was Fickian diffusion.
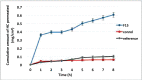
Conclusion: The simulated pharmacokinetic parameters showed that F15 had the highest AUC, MDT, and DE. Furthermore, F15 significantly enhanced HC permeation by 12-folds compared to the control through the excised rat's skin. The skin irritancy test has proven F15 safety and skin compatibility.
Keywords: DDSolver; Transfersomes; edge activator; hydrocortisone; in vitro release; permeation; transdermal.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimization of elastic transfersomes formulations for transdermal delivery of pentoxifylline.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016 May;102:101-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016. PMID: 26925505
-
Response Surface Optimization of Ultra-Elastic Nanovesicles Loaded with Deflazacort Tailored for Transdermal Delivery: Accentuated Bioavailability and Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jan 25;16:591-607. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S276330. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33531803 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical design and optimization of nano-transfersomes based chitosan gel for transdermal delivery of cefepime.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2024 Jun;50(6):511-523. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2024.2353098. Epub 2024 May 21. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38718267
-
Overcoming Skin Barrier with Transfersomes: Opportunities, Challenges, and Applications.Curr Drug Deliv. 2025;22(2):160-180. doi: 10.2174/0115672018272012231213100535. Curr Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 38178667 Review.
-
Transfersomes: a Revolutionary Nanosystem for Efficient Transdermal Drug Delivery.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Dec 1;23(1):7. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02166-9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 34853906 Review.
Cited by
-
Solid dispersion systems for enhanced dissolution of poorly water-soluble candesartan cilexetil: In vitro evaluation and simulated pharmacokinetics studies.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 6;19(6):e0303900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303900. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38843120 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and In Vivo Evaluation of In Situ pH-Sensitive Hydrogel of Sonidegib-Invasomes via Intratumoral Delivery for Basal Cell Skin Cancer Management.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 30;18(1):31. doi: 10.3390/ph18010031. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39861094 Free PMC article.
-
Pomegranate extract-loaded sphingosomes for the treatment of cancer: Phytochemical investigations, formulation, and antitumor activity evaluation.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 12;19(2):e0293115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293115. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38346085 Free PMC article.
-
L-Cysteine-Modified Transfersomes for Enhanced Epidermal Delivery of Podophyllotoxin.Molecules. 2023 Jul 28;28(15):5712. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155712. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul Rasool B.K., Mohammed A.A., Salem Y.Y. The optimization of a dimenhydrinate transdermal patch formulation based on the quantitative analysis of in vitro release data by DDSolver through skin penetration studies. Sci. Pharm. 2021;89:33. doi: 10.3390/scipharm89030033. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

