Blockchain and K-Means Algorithm for Edge AI Computing
- PMID: 35676965
- PMCID: PMC9168108
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1153208
Blockchain and K-Means Algorithm for Edge AI Computing
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Blockchain and K-Means Algorithm for Edge AI Computing.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9867367. doi: 10.1155/2023/9867367. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37538569 Free PMC article.
Abstract
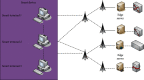
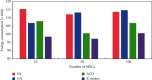
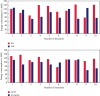
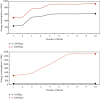
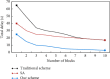
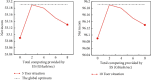
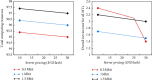
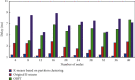
The current development of blockchain, technically speaking, still faces many key problems such as efficiency and scalability issues, and any distributed system faces the problem of how to balance consistency, availability, and fault tolerance need to be solved urgently. The advantage of blockchain is decentralization, and the most important thing in a decentralized system is how to make nodes reach a consensus quickly. This research mainly discusses the blockchain and K-means algorithm for edge AI computing. The natural pan-central distributed trustworthiness of blockchain provides new ideas for designing the framework and paradigm of edge AI computing. In edge AI computing, multiple devices running AI algorithms are scattered across the edge network. When it comes to decentralized management, blockchain is the underlying technology of the Bitcoin system. Due to its characteristics of immutability, traceability, and consensus mechanism of transaction data storage, it has recently received extensive attention. Blockchain technology is essentially a public ledger. This is done by recording data related to trust management to this ledger. To collaboratively complete artificial intelligence computing tasks or jointly make intelligent group decisions, frequent communication is required between these devices. By integrating idle computing resources in an area, a distributed edge computing platform is formed. Users obtain benefits by sharing their computing resources, and nodes in need complete computing tasks through the shared platform. In view of the identity security problems faced in the sharing process, this article introduces blockchain technology to realize the trust between users. All participants must register a secure identity in the blockchain network and conduct transactions in this security system. A K-means algorithm suitable for edge environments is proposed to identify different degradation stages of equipment operation reflected by multiple types of data. Based on the prediction of the fault state for a single type of data, the algorithm uses the historical data of multiple types of data together with the prediction data to predict the fault stage. During the research process, the average optimization energy consumption of K-means algorithm is 14.6% lower than that of GA. On the basis of designing a resource allocation scheme based on blockchain, the problem of how the participants can realize reliable resource use according to the recorded data on the chain is studied. The article implements the verification of the legality of the use of blockchain resources. In addition, a control node is introduced to master the global real-time information of the network to provide data support for the user's choice.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaotian Qiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang Q., Yang L. T., Chen Z., Xia F. A high-order possibilistic C-means algorithm for clustering incomplete multimedia data. IEEE Systems Journal . 2017;11(4):2160–2169. doi: 10.1109/jsyst.2015.2423499. - DOI
-
- Kumar A., Kumar D., Jarial S. K. A hybrid clustering method based on improved artificial bee colony and fuzzy C-means algorithm. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence . 2017;15(2):40–60.
-
- Alsmadi M. K. A hybrid Fuzzy C-Means and Neutrosophic for jaw lesions segmentation. Ain Shams Engineering Journal . 2018;9(4):697–706. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2016.03.016. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

