Memory B Cell Activation Induced by Pertussis Booster Vaccination in Four Age Groups of Three Countries
- PMID: 35677044
- PMCID: PMC9168128
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.864674
Memory B Cell Activation Induced by Pertussis Booster Vaccination in Four Age Groups of Three Countries
Abstract
Background: Immunogenicity of acellular pertussis (aP) vaccines is conventionally assessed by measuring antibody responses but antibody concentrations wane quickly after vaccination. Memory B cells, however, are critical in sustaining long-term protection and therefore may be an important factor when assessing pertussis immunity after vaccination.
Aim: We studied pertussis specific memory B cell (re)activation induced by an aP booster vaccination in four different age groups within three countries.
Materials and methods: From a phase IV longitudinal interventional study, 268 participants across Finland, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom were included and received a 3-component pertussis booster vaccine: children (7-10y, n=53), adolescents (11-15y, n=66), young adults (20-34y, n=74), and older adults (60-70y, n=75). Memory B cells at baseline, day 28, and 1 year post-vaccination were measured by a pertussis toxin (Ptx), filamentous haemagglutinin (FHA), and pertactin (Prn) specific ELISpot assay. Antibody results measured previously were available for comparison. Furthermore, study participants were distributed into groups based on their baseline memory B cell frequencies, vaccine responses were monitored between these groups.
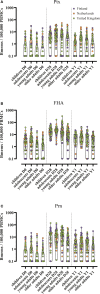
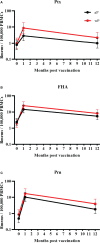
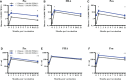
Results: Geometric mean (GM) memory B cell frequencies for pertussis antigens at baseline were low. At 28 days post-vaccination, these frequencies increased within each age group and were still elevated one year post-booster compared to baseline. Highest frequencies at day 28 were found within adolescents (GM: 5, 21, and 13, for Ptx, FHA and Prn, respectively) and lowest within older adults (GM: 2, 9, and 3, respectively). Moderate to strong correlations between memory B cell frequencies at day 28 and antibody concentrations at day 28 and 1 year were observed for Prn. Memory B cell frequencies > 1 per 100,000 PBMCs at baseline were associated with significantly higher memory responses after 28 days and 1 year.
Conclusions: An aP booster vaccine (re)activated memory B cells in all age groups. Still elevated memory B cell frequencies after one year indicates enhanced immunological memory. However, antigen specific memory B cell activation seems weaker in older adults, which might reflect immunosenescence. Furthermore, the presence of circulating memory B cells at baseline positively affects memory B cell responses. This study was registered at www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu: No. 2016-003678-42.
Keywords: pertussis; adolescents; adults; children; longitudinal; memory B cells; older adults; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Versteegen, Barkoff, Valente Pinto, van de Kasteele, Knuutila, Bibi, de Rond, Teräsjärvi, Sanders, de Zeeuw-Brouwer, Luoto, ten Hulscher, Clutterbuck, Sanders, Mertsola, Berbers, He, Kelly, Buisman and PERISCOPE Consortium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

