Lactobacillus: Friend or Foe for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus?
- PMID: 35677055
- PMCID: PMC9168270
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.883747
Lactobacillus: Friend or Foe for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus?
Abstract
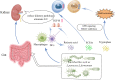
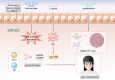
The cause of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) remains largely unknown, despite the fact that it is well understood that a complex interaction between genes and environment is required for disease development. Microbiota serve as activators and are essential to immune homeostasis. Lactobacillus is thought to be an environmental agent affecting the development of SLE. However, beneficial therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus on SLE were also explored. The discovery of Lactobacillus involvement in SLE will shed light on how SLE develops, as well as finding microbiota-targeted biomarkers and novel therapies. In this review, we attempt to describe the two sides of Lactobacillus in the occurrence, development, treatment and prognosis of SLE. We also discuss the effect of different strains Lactobacillus on immune cells, murine lupus, and patients. Finally, we try to illustrate the potential immunological mechanisms of Lactobacillus on SLE and provide evidence for further microbiota-targeted therapies.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; immunoregulators; microbiota; pathogenesis; systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Fan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of microbiota in the pathogenesis of lupus: Dose it impact lupus nephritis?Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jan;139:191-198. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.023. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30471408 Review.
-
Gut Microbiome and Metabolites in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Link, Mechanisms and Intervention.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 15;12:686501. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686501. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34335588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal microbiota and active systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review.Adv Rheumatol. 2021 Jul 2;61(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s42358-021-00201-8. Adv Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34215348
-
Recent Advances in Our Understanding of the Link between the Intestinal Microbiota and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 30;20(19):4871. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194871. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31575045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Novel Insights into Mechanisms and Promising Therapeutic Strategies.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 3;12:799788. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.799788. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Racial Differences in Plasma Microbial Translocation and Plasma Microbiome, Implications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Pathogenesis.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024 Jun;6(6):365-374. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11664. Epub 2024 Apr 2. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38563441 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D: An Essential Nutrient in the Dual Relationship between Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases and Celiac Disease-A Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 4;16(11):1762. doi: 10.3390/nu16111762. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new generation of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells differentially trained by immunoregulatory probiotics in a lupus microenvironment.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Dec 10;14(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03578-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38072921 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering potential biomarkers and metabolic pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis through integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis.BMC Microbiol. 2025 May 7;25(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03995-5. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40329182 Free PMC article.
-
Immune metabolic restoration in systemic lupus erythematosus: the impact of gut microbiota, probiotics, and nutritional synergy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1602235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602235. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40534849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsioni V, Andreoli L, Meini A, Frassi M, Raffetti E, Airò P, et al. . The Prevalence and Incidence of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Adults: A Population-Based Study in a Mountain Community in Northern Italy. Clin Exp Rheumatol (2015) 33:681–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

