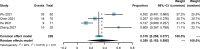The Significance of Transarterial Chemo(Embolization) Combined With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Era of Systemic Therapy: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35677059
- PMCID: PMC9167927
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.913464
The Significance of Transarterial Chemo(Embolization) Combined With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Era of Systemic Therapy: A Systematic Review
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The Significance of Transarterial Chemo(embolization) Combined With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Immune Check Point Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Era of Systemic Therapy: A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 7;13:952446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.952446. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35747141 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background and aims: Regardless of great progress in early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), unresectable HCC (uHCC) still accounts for the majority of newly diagnosed HCC with poor prognosis. With the promising results of a double combination of transarterial chemo(embolization) and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), and TKIs and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), a more aggressive strategy, a triple combination of transarterial chemo(embolization), TKIs, and ICIs has been tried in the recent years. Hence, we aimed to conduct a systematic review to verify the safety and efficacy of the triple therapy for uHCC.
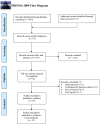
Methods: PubMed, MedLine, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Knowledge were used to screen the eligible studies evaluating the clinical efficacy and safety of triple therapy for patients with uHCC up to April 25th 2022, as well as Chinese databases. The endpoints were the complete response (CR), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), conversion rate, progression-free survival (PFS) rate, overall survival (OS) rate, and the incidence of adverse events (AEs).
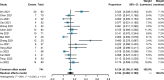
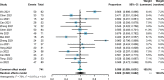
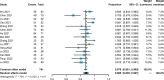
Results: A total of 15 studies were eligible with 741 patients receiving transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) or hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) combined with TKIs and ICIs. The pooled rate and 95% confidence interval (CI) for CR, ORR, and DCR were 0.124 (0.069-0.190), 0.606 (0.528-0.682), and 0.885 (0.835-0.927). The pooled rates for PFS at 0.5 years and 1 year were 0.781 (0.688-0.862) and 0.387 (0.293-0.486), respectively. The pooled rates for OS at 1, 2, and 3 years were 0.690 (0.585-0.786), 0.212 (0.117-0.324), and 0.056 (0.028-0.091), respectively. In addition, the pooled rate and 95%CI for the conversion surgery was 0.359 (0.153-0.595). The subgroup analysis of control studies showed that triple therapy was superior to TACE+TKIs, TKIs+ICIs, and TKIs in CR, ORR, and DCR, conversion rate; PFS; and OS. No fatal AEs were reported, and the top three most common AEs were elevated ALT, elevated AST, and hypertension, as well as severe AEs (grading ≥3).
Conclusion: With the current data, we concluded that the triple therapy of TACE/HAIC, TKIs, and ICIs would provide a clinical benefit for uHCC both in short- and long-term outcomes without increasing severe AEs, but the conclusion needs further validation.
Systematic review registration: http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, Review registry: CRD42022321970.
Keywords: hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune checkpoint inhibitors; systematic review; transarterial chemotherapy; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2022 Ke, Xin, Fang, Zeng, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors versus tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors alone in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Apr 7;23(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03788-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40197348 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization: Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors With or Without Programmed Cell Death Protein-1 Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma-A Retrospective Study.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Nov;31(12):7860-7869. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15933-2. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39090499
-
Immunotherapy improved the efficacy of TACE or TACE plus MTTs in HCC patients: A meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Feb 6;147:114006. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.114006. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39793227 Review.
-
Triple combination of HAIC-FO plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 16;18(10):e0290644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290644. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37844117 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world efficacy and safety of TACE-HAIC combined with TKIs and PD-1 inhibitors in initially unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112492. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112492. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38906005
Cited by
-
Outcomes and prognostic factors in initially unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated using conversion therapy with lenvatinib and TACE plus PD-1 inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 30;13:1110689. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1110689. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36793614 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Survival Outcomes of Liver Resection following Triple Combination Conversion Therapy for Initially Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 17;15(24):5878. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245878. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136422 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma without macrovascular invasion or extrahepatic metastasis: analysis of factors prognostic of clinical outcomes.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 6;13:1072922. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1072922. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37346065 Free PMC article.
-
Liver transplantation following two conversions in a patient with huge hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein invasion: A case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 28;30(36):4071-4077. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i36.4071. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39351247 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, safety, and biomarker analysis of TACE combined with lenvatinib plus sintilimab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a real-world study.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Nov 5;74(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03857-5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39499356 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous