Diosgenin: An Updated Pharmacological Review and Therapeutic Perspectives
- PMID: 35677108
- PMCID: PMC9168095
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1035441
Diosgenin: An Updated Pharmacological Review and Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
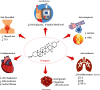
Plants including Rhizoma polgonati, Smilax china, and Trigonella foenum-graecum contain a lot of diosgenin, a steroidal sapogenin. This bioactive phytochemical has shown high potential and interest in the treatment of various disorders such as cancer, diabetes, arthritis, asthma, and cardiovascular disease, in addition to being an important starting material for the preparation of several steroidal drugs in the pharmaceutical industry. This review aims to provide an overview of the in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies reporting the diosgenin's pharmacological effects and to discuss the safety issues. Preclinical studies have shown promising effects on cancer, neuroprotection, atherosclerosis, asthma, bone health, and other pathologies. Clinical investigations have demonstrated diosgenin's nontoxic nature and promising benefits on cognitive function and menopause. However, further well-designed clinical trials are needed to address the other effects seen in preclinical studies, as well as a better knowledge of the diosgenin's safety profile.
Copyright © 2022 Prabhakar Semwal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anticancer Activity of Diosgenin and Its Molecular Mechanism.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Aug;29(8):738-749. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3693-1. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36940072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Diosgenin and Its Major Derivatives against Neurological Diseases: Recent Advances.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 6;2020:3153082. doi: 10.1155/2020/3153082. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32215172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diosgenin: Recent Highlights on Pharmacology and Analytical Methodology.J Anal Methods Chem. 2016;2016:4156293. doi: 10.1155/2016/4156293. Epub 2016 Dec 28. J Anal Methods Chem. 2016. PMID: 28116217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diosgenin, a steroid saponin of Trigonella foenum graecum (Fenugreek), inhibits azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypt foci formation in F344 rats and induces apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004 Aug;13(8):1392-8. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004. PMID: 15298963
-
Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum-Graecum) Seed Flour and Diosgenin Preserve Endothelium-Dependent Arterial Relaxation in a Rat Model of Early-Stage Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 10;19(3):798. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030798. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29534453 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Safety of Innovative Nanotechnology Oral Formulations Loaded with Bioactive Menopause Molecules: Influence of Genotoxicity and Biochemical Parameters on a Menopausal Rat Model.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 29;15(23):4951. doi: 10.3390/nu15234951. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38068809 Free PMC article.
-
Recent updates on anticancer mechanisms of polyphenols.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 29;10:1005910. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1005910. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36247004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural essential oils as a new therapeutic tool in colorectal cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 13;22(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02806-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36514100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How reliable is the labeling of a commercial phytosteroid product? A 12-week randomized double-blind training study.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2540408. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2025.2540408. Epub 2025 Aug 8. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40781783 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sesquiterpenoid lactones as potential anti-cancer agents: an update on molecular mechanisms and recent studies.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Oct 7;22(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02721-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36207736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

