Analysis of the Underlying Mechanism of the Jiu Wei Zhen Xin Formula for Treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder Based on Network Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- PMID: 35677384
- PMCID: PMC9168090
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7761852
Analysis of the Underlying Mechanism of the Jiu Wei Zhen Xin Formula for Treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder Based on Network Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Abstract
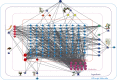
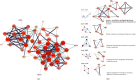
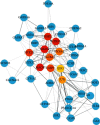
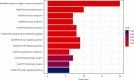
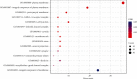
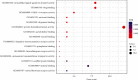
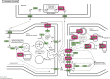
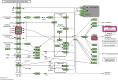
Currently, there are many effective pharmacological treatments for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), formulated herbal granule is also an alternative way. Our research intends to construct a pharmacological network on genetic targets and pathways between Jiu Wei Zhen Xin Formula (JWZXF) and GAD. Through the TCMSP database, we collected the active ingredients of JWZXF and potential targets of the active ingredients. The GAD-related proteins collected from GeneCards database and DisGeNET database were combined. Component-target protein networks were constructed and visualized using Cytoscape 3.8.2 software to comprehensively clarify the relationships between ingredients, components, and targets. The intersection targets were imported into the STRING database, and the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed. We constructed and analyzed the visualized "drug-target-disease" network. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment together with Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis were conducted on the common target through R language. Forty-one effective components and 106 potential targets of JWZXF were found. There were top ten hub genes and multiple important signaling pathways involved in the treatment of GAD with the JWZXF. This study expounded the pharmacological actions and molecular mechanisms of the JWZXF in treating GAD from a holistic perspective. The potential pharmacological effects of the JWZXF are closely related to regulation because not only does it comprehensively analyze the possible mechanism of JWZXF treatment of GAD but it can also facilitate further in-depth research and provide a theoretical basis for the clinical expansion of its application.
Copyright © 2022 Heng Shao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking-based analyses to predict the potential mechanism of Huangqin decoction in treating colorectal cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jul 6;11(19):4553-4566. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4553. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37469733 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacology approach to determine the underlying mechanisms of action of Yishen Tongluo formula for the treatment of oligoasthenozoospermia.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 21;16(6):e0252906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252906. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34153045 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Network Pharmacology-based Strategy to Investigate Pharmacological Mechanisms of Qingbutongluo Pill for Treatment of Brucellosis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(4):706-718. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220609121842. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 35692141
-
Network pharmacology-based identification of miRNA expression of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Feb 4;101(5):e28747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028747. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35119030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anxiety in oncology outpatients is associated with perturbations in pathways identified in anxiety focused network pharmacology research.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Nov 28;31(12):727. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-08196-2. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38012456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental disorders:DSM-5 . 5th. Arlington, TX, USA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. pp. 222–226.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

