Functional foods: promising therapeutics for Nigerian Children with sickle cell diseases
- PMID: 35677416
- PMCID: PMC9167986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09630
Functional foods: promising therapeutics for Nigerian Children with sickle cell diseases
Abstract
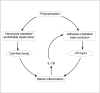
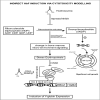
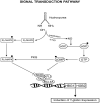
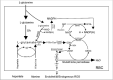
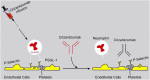
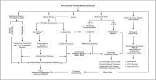
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also known as sickle cell anemia (SCA) is one of the structural hemoglobinopathies that occurs due to a single nucleotide mutation from GAG to GTG, which changes the amino acid of a β-globin chain of hemoglobin (Hb) from glutamate to valine. This singular mutation results to disorderliness in red blood cells (RBCs) with advent of changes in RBC morphology and other pathological conditions. In the 1980s, intermittent red blood cell transfusions, opioids, and penicillin prophylaxis were the only available therapy for SCA and were commonly reserved for acute, life threatening complications. So far, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted a total of four drugs approval for the prophylaxis and treatment of the clinical complications of SCD. Due to limitations (adherence, safety, adverse effects) of existing therapies in the prophylaxis and treatment of SCD complications in Nigerian children and their inaccessibility to approved drugs, the present study discusses the therapeutic effects of readily available functional food as one of the therapies or an adjunct therapy to tackle the sickle cell crisis in Nigerian Children.
Keywords: Functional foods; Pediatric/children; Sickle cell disease (SCD).
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sickle Cell Disease: Current Drug Treatments and Functional Foods with Therapeutic Potential.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 12;46(6):5845-5865. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060349. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Sickle Cell Disease.2023 Jul 19. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Jul 19. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30860750 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sickle cell disease: progress towards combination drug therapy.Br J Haematol. 2021 Jul;194(2):240-251. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17312. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 33471938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction/hyperhemolysis syndrome in children with sickle cell disease.Pediatrics. 2003 Jun;111(6 Pt 1):e661-5. doi: 10.1542/peds.111.6.e661. Pediatrics. 2003. PMID: 12777582
-
Management of sickle cell disease: summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members.JAMA. 2014 Sep 10;312(10):1033-48. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.10517. JAMA. 2014. PMID: 25203083 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation of the Anti-Sickle Cell Activity of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Two Medicinal Plants from Niger: Flueggea virosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) Royle and Kigelia africana (Lam.) Benth.Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;12(20):3522. doi: 10.3390/plants12203522. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895986 Free PMC article.
-
Sickle Cell Disease: Current Drug Treatments and Functional Foods with Therapeutic Potential.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 12;46(6):5845-5865. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060349. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bunn H.F. Pathogenesis and treatment of sickle cell disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;337(11):762–769. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg M.H. Sickle cell disease. Hematology. 2004;1:53.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

