Role of Licochalcone A in Potential Pharmacological Therapy: A Review
- PMID: 35677438
- PMCID: PMC9168596
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.878776
Role of Licochalcone A in Potential Pharmacological Therapy: A Review
Abstract
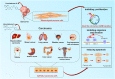
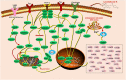
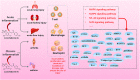
Licochalcone A (LA), a useful and valuable flavonoid, is isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. ex DC. and widely used clinically in traditional Chinese medicine. We systematically updated the latest information on the pharmacology of LA over the past decade from several authoritative internet databases, including Web of Science, Elsevier, Europe PMC, Wiley Online Library, and PubMed. A combination of keywords containing "Licochalcone A," "Flavonoid," and "Pharmacological Therapy" was used to help ensure a comprehensive review. Collected information demonstrates a wide range of pharmacological properties for LA, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-parasitic, bone protection, blood glucose and lipid regulation, neuroprotection, and skin protection. LA activity is mediated through several signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt/mTOR, P53, NF-κB, and P38. Caspase-3 apoptosis, MAPK inflammatory, and Nrf2 oxidative stress signaling pathways are also involved with multiple therapeutic targets, such as TNF-α, VEGF, Fas, FasL, PI3K, AKT, and caspases. Recent studies mainly focus on the anticancer properties of LA, which suggests that the pharmacology of other aspects of LA will need additional study. At the end of this review, current challenges and future research directions on LA are discussed. This review is divided into three parts based on the pharmacological effects of LA for the convenience of readers. We anticipate that this review will inspire further research.
Keywords: anticancer; flavonoid; licochalcone A; pharmacological therapy; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Xie, Jiang, Huang, Tong, Li, Xie and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida Fontes L. B., Aarestrup B. J. V., Aarestrup F. M., Da Silva Filho A. A., do Amaral Correa J. O. (2014a). Effects of Licochalcone A on Immunomodulation in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Planta Medica 80 (16), 1403. 10.1055/s-0034-1394634 - DOI
-
- Angelova-Fischer I., Neufang G., Jung K., Fischer T. W., Zillikens D. (2014). A Randomized, Investigator-Blinded Efficacy Assessment Study of Stand-Alone Emollient Use in Mild to Moderately Severe Atopic Dermatitis Flares. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol Venereol. 28 (Suppl. 3), 9–15. 10.1111/jdv.12479 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angelova-Fischer I., Rippke F., Richter D., Filbry A., Arrowitz C., Weber T., et al. (2018). Stand-alone Emollient Treatment Reduces Flares after Discontinuation of Topical Steroid Treatment in Atopic Dermatitis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Vehicle-Controlled, Left-Right Comparison Study. Acta Derm. Venereol. 98 (5), 517–523. 10.2340/00015555-2882 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

