A Prospective Five-Year Follow-up After peg-Interferon Plus Nucleotide Analogue Treatment or no Treatment in HBeAg Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- PMID: 35677522
- PMCID: PMC9168707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.12.011
A Prospective Five-Year Follow-up After peg-Interferon Plus Nucleotide Analogue Treatment or no Treatment in HBeAg Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
Abstract
Background: Currently available treatment options for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) are not recommended for HBeAg-negative patients with a low viral load. These patients may however benefit from treatment by achieving a functional cure, defined by HBsAg-loss and undetectable HBV DNA. This study evaluated the long-term effect of combination treatment with peg-interferon-alpha-2a (peg-IFN) and adefovir or tenofovir compared to no treatment in these patients.
Methods: HBeAg-negative CHB patients with HBV-DNA levels < 20,000 IU/mL (n = 151) were previously randomised 1:1:1 for peg-IFN 180 μg/week plus either adefovir 10 mg/day or tenofovir 245 mg/day, or no treatment and treated for 48 weeks in an open-label study. In this prospective long-term follow-up study, patients were monitored yearly up to five years after end of treatment (week 308). The primary outcome was sustained HBsAg-loss and secondary outcome the dynamics of HBsAg and HBV-DNA levels over time.
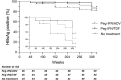
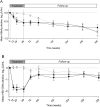
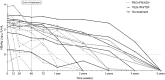
Results: Of the 131 followed patients, the HBsAg-status was known for 118 patients after five-year follow-up. HBsAg-loss occurred similarly (P = 0.703) in all arms: 8/43 (18.6%) peg-IFN + adefovir, 4/34 (11.7%) peg-IFN + tenofovir, and 6/41 (14.6%) among the untreated patients. The time to HBsAg-loss did not differ between groups (P = 0.641). Low baseline HBsAg levels and genotype A were independently associated with HBsAg-loss irrespective of allocation. HBsAg and HBV-DNA levels declined similarly during follow-up in all patient groups.
Conclusions: This prospective randomised controlled study showed that HBsAg-loss overtime was not influenced by treatment with a combination of nucleotide analogue and Peg-IFN. Low baseline HBsAg levels can predict HBsAg-loss irrespective of treatment allocation.
Keywords: ADV, Adefovir dipivoxil; ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; CHB, Chronic hepatitis B; EOT, End of treatment; GZ, Grey zone; HBeAg, Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg, Hepatitis B surface antigen; HCC, Hepatocellular Carcinoma; HNCH, HBeAg-negative chronic infection; NA, Nucleot(s)ide analogue; ROC, Receiver operating characteristic; TAF, Tenofovir alafenamide fumarateor; TDF, Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate; ULN, Upper limit of normal; UMC, University Medical Centers; combination therapy; functional cure; hepatitis B virus; inactive carrier; low viral load; peg-IFN, Pegylated-interferon.
© 2022 Indian National Association for Study of the Liver.
Figures
References
-
- Razavi-Shearer D., Gamkrelidze I., Nguyen M.H., et al. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:383–403. - PubMed
-
- Wedemeyer H., Schöneweis K., Voronkova N., Chulanov V. vol. 70. 2019. Safety and efficacy of 10mg (high-dose) bulevirtide (Myrcludex B) in combination with peg-interferon alpha 2a or tenofovir in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection: week 24 interim results of the MYR203 extension study; pp. 58A–59A. (Hepatology, AASLD liver meeting). [Abstract 85]
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver Electronic address eee, European association for the study of the L. EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017;67:370–398. - PubMed
-
- Fattovich G., Bortolotti F., Donato F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 2008;48:335–352. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

