Stakeholder Network Analysis for Front-of-Pack Labeling in China
- PMID: 35677544
- PMCID: PMC9169156
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.871062
Stakeholder Network Analysis for Front-of-Pack Labeling in China
Abstract
Background: Front-of-pack (FoP) labeling on packaged foods is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) to reduce diet-related non-communicable diseases, but it has not yet been implemented in China. The introduction of FoP labeling is driven by multiple institutions and stakeholders. This study aimed to identify key institutional actors involved in FoP labeling and describe links between actors to support future FoP labeling policies and programmes in China.
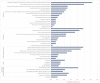
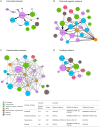
Methods: The Net-Map method was adopted. We conducted Net-map activities with eight participants using face-to-face interviews between November 2020 and May 2021. Participants were asked to identify actors involved in the development and implementation of FoP labeling in China, describe networks among actors according to pre-defined link types (command, dissemination, funding, and technical assistance), and estimate influence of each actor within the FoP labeling landscape. Social network analysis measures of cohesion and centrality were used to describe each network. Gephi software was used for social network analysis and network visualization.
Results: Forty-one unique actors were identified across seven actor categories including government agencies (n = 14), technical support agencies (n = 7), professional associations (n = 10), food industry groups (n = 2), media groups (n = 4), international organizations (n = 3), and a consumer group (n = 1). Weighted influence scores among actors ranged from 0.13 to 3.13. The Department of Food Safety Standards, Risk Surveillance and Assessment of the National Health Commission (DFSSRSA of NHC) was the actor with the highest weighted influence score, followed by the Bureau of Disease Prevention and Control of National Health Commission, Chinese Nutrition Society, and the National Institute for Nutrition and Health of Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. DFSSRSA of NHC played a central role in both command and technical assistance networks. State-owned media had the greatest betweenness and outdegree centrality in the dissemination network. The Chinese Nutrition Society was in the central position and provided funding to diverse actors in the funding network.
Conclusions: A variety of multisectoral actors have an interest in the introduction of FoP labeling policies and programmes. Effectively engaging key actors identified in this study can generate a multisectoral commitment to advance FoP labeling policies and programmes in China.
Keywords: China; Net-map; front-of-package labeling; network analysis; stakeholder analysis; stakeholder mapping.
Copyright © 2022 Yin, Ye, Xin, Xiang, Yu, Yan, Wen, Tian, Jones, Pettigrew and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Martinez R, Lloyd-Sherlock P, Soliz P, Ebrahim S, Vega E, Ordunez P, et al. Trends in premature avertable mortality from non-communicable diseases for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a population-based study. Lancet Glob Health. (2020) 8:e511–23. 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30035-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Organization WH . Tackling NCDs:'Best Buys' and Other Recommended Interventions for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. World Health Organization; (2017).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

