Very Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet Improves Risk Markers for Cardiometabolic Health More Than Exercise in Men and Women With Overfat Constitution: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35677551
- PMCID: PMC9168912
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.867690
Very Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet Improves Risk Markers for Cardiometabolic Health More Than Exercise in Men and Women With Overfat Constitution: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: This randomized controlled parallel-group study examined the effects of a very low-carbohydrate high-fat (VLCHF) diet and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) program over 12-weeks on cardiometabolic risk factors in individuals with overfat constitution.
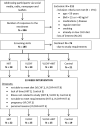
Methods: Ninety-one participants out of 109 completed the study. The participants were randomly allocated to the HIIT (N = 22), VLCHF (N = 25), VLCHF+HIIT (N = 25), or control (N = 19) groups for 12 weeks. Fasting plasma samples were collected before the intervention and after 4 and 12 weeks. The analyzed outcomes included complete blood count, glucose, insulin, glycated hemoglobin, triglycerides (TG), cholesterol, high- and low-density lipoprotein (HDL-C and LDL-C), lipoprotein(a), adiponectin (Adpn), leptin (Lep), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), other interleukins (hs-IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-10), and IL-1RA. The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), Adpn/Lep ratio, TG/HDL-C ratio, and TyG index were calculated and analyzed. Blood pressure was measured before the intervention, after 4, 8, and 12 weeks (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03934476).
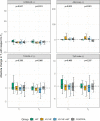
Results: Absolute changes in HOMA-IR, Adpn/Lep ratio, LDL-C, and diastolic blood pressure after 12 weeks differed by study groups (p < 0.05). The most pronounced changes were revealed in the VLCHF (ΔM [95% CI]; HOMA-IR: -0.75 [-1.13; -0.55]; Adpn/Lep: 9.34 [6.33; 37.39]; LDL-C: 0.06 [-0.12; 0.50] mmol/l) and VLCHF+HIIT (HOMA-IR: -0.44 [-1.14; 0.12]; Adpn/Lep: 4.26 [2.24; 13.16]; LDL-C: 0.25 [-0.04; 0.50] mmol/l) groups.
Conclusions: A 12-week VLCHF diet intervention in individuals with overfat constitution is effective for favorable changes in HOMA-IR (compared to HIIT), Adpn/Lep ratio, and diastolic blood pressure. HIIT, or HIIT combined with the VLCHF diet, had no additional benefits for the analyzed variables. No adverse side effects were observed.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; TG/HDL-C; TyG index; adiponectin; exercise; leptin; low carbohydrate diet; overfat.
Copyright © 2022 Cipryan, Litschmannova, Maffetone, Plews, Dostal, Hofmann and Laursen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of a Very Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet and High-Intensity Interval Training on Visceral Fat Deposition and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Overfat Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Front Nutr. 2021 Dec 21;8:785694. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.785694. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34993222 Free PMC article.
-
A lipidomic and metabolomic signature of a very low-carbohydrate high-fat diet and high-intensity interval training: an additional analysis of a randomized controlled clinical trial.Metabolomics. 2023 Dec 23;20(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s11306-023-02071-1. Metabolomics. 2023. PMID: 38141101 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adiponectin/leptin ratio increases after a 12-week very low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, and exercise training in healthy individuals: A non-randomized, parallel design study.Nutr Res. 2021 Mar;87:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.12.012. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 33596508 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of high-intensity interval training on cardiometabolic risk factors in childhood obesity: a meta-analysis.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2021 May;61(5):743-752. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.20.11329-X. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2021. PMID: 33975429
-
A Meta-Analysis of High-Intensity Interval Training on Glycolipid Metabolism in Children With Metabolic Disorders.Front Pediatr. 2022 May 12;10:887852. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.887852. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35633975 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Obesity and Obesity-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Any Potential Role for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD)?Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Jun;13(2):194-213. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00528-w. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 38526760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of very low-carbohydrate high-fat diet and high-intensity interval training on mental health-related indicators in individuals with excessive weight or obesity.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 14;14(1):28023. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79378-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39543330 Free PMC article.
-
Lifestyle and Lipoprotein(a) Levels: Does a Specific Counseling Make Sense?J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 28;13(3):751. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030751. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet: What Effects on Lipid Metabolism?Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Sep;13(3):516-526. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00556-6. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 39008211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of ketogenic diet on adipokines levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Dec;61(12):1495-1510. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02362-6. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39302468
References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention NC for HS . Health, United States, 2015: With Special Feature on Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities. Hyattsville, MD: Frontiers in Public Health; (2016).
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous