Effects of dandelion addition on antioxidant property, sensory characteristics and inhibitory activity against xanthine oxidase of beer
- PMID: 35677651
- PMCID: PMC9168054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.05.008
Effects of dandelion addition on antioxidant property, sensory characteristics and inhibitory activity against xanthine oxidase of beer
Abstract
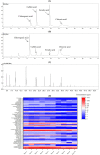
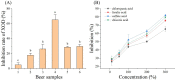
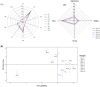
The effects of dandelion addition (DA) on the physiochemical properties, antioxidant activity, inhibitory activity against xanthine oxidase (XOD) and flavor of craft beer were investigated. It was found that DA changed the pH value, total acid content, thiobarbituric-acid-value, sugar content and color of beer, and increased the contents of total polyphenols and flavonoids and thus the antioxidant activity of beer. HPLC analysis showed that DA provided beer with chlorogenic, caffeic, ferulic, and chicoric acid, contributing to the inhibition activity against XOD that is a key enzyme in uric acid production. GC-MS analysis showed that 3-methyl-1-butanol, isopentyl acetate and ethyl caprylate were main aroma components of all samples. Although DA introduced the special aroma component of azulene, it did not significantly affect the appearance, bubble, aroma and taste evaluation of beer. Conclusively, DA potentially improved the beer properties of antioxidant and inhibition of uric acid production without changing its sensory characteristics.
Keywords: Antioxidant activity; Chicoric acid; Craft beer; Dandelion; Polyphenols; Xanthine oxidase.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of tea addition on antioxidant capacity, volatiles, and sensory quality of beer.Food Chem X. 2024 Feb 4;21:101193. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101193. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38357372 Free PMC article.
-
Use of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaves as beer ingredient, and their influence on beer chemical composition and antioxidant activity.J Food Sci. 2020 Aug;85(8):2278-2285. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15318. Epub 2020 Jul 11. J Food Sci. 2020. PMID: 32652593
-
Phenolics Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Special Beers.Molecules. 2020 May 26;25(11):2466. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112466. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32466403 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of interaction of tannins with co-existing substances. VII. Inhibitory effects of tannins and related polyphenols on xanthine oxidase.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1990 May;38(5):1224-9. doi: 10.1248/cpb.38.1224. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1990. PMID: 2393948
-
Overview of craft brewing specificities and potentially associated microbiota.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(3):462-473. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1378616. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 28910550 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological Mechanisms by Which the Functional Ingredients in Beer Impact Human Health.Molecules. 2024 Jun 29;29(13):3110. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133110. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium and Evaluation of Their Uric Acid-Lowering Activity.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025 Mar 21;80(2):97. doi: 10.1007/s11130-025-01337-4. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40117004
-
Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale): A Promising Source of Nutritional and Therapeutic Compounds.Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2025;16(1):41-56. doi: 10.2174/012772574X293072240217185616. Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2025. PMID: 38425109 Review.
References
-
- Ahmed Q.U., Alhassan A.M., Khatib A., Shah S.A.A., Hasan M.M., Sarian M.N. Antiradical and Xanthine Oxidase inhibitory activity evaluations of averrhoa bilimbi L. Leaves and tentative identification of bioactive constituents through LC-QTOF-MS/MS and molecular docking approach. Antioxidants. 2018;7(10):137–153. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Callemien D., Collin S. Structure, organoleptic properties, quantification methods, and stability of phenolic compounds in beer-A review. Food Rev. Int. 2009;26(1):1–84. doi: 10.1080/87559120903157954. - DOI
-
- Ceccaroni D., Sileoni V., Marconi O., De Francesco G., Lee E.G., Perretti G. Specialty rice malt optimization and improvement of rice malt beer aspect and aroma. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 2019;99:299–305. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.09.060. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

