Early Developmental PMCA2b Expression Protects From Ketamine-Induced Apoptosis and GABA Impairments in Differentiating Hippocampal Progenitor Cells
- PMID: 35677757
- PMCID: PMC9167922
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.890827
Early Developmental PMCA2b Expression Protects From Ketamine-Induced Apoptosis and GABA Impairments in Differentiating Hippocampal Progenitor Cells
Abstract
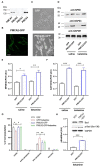
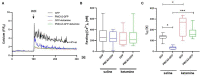
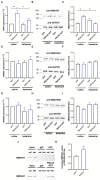
PMCA2 is not expressed until the late embryonic state when the control of subtle Ca2+ fluxes becomes important for neuronal specialization. During this period, immature neurons are especially vulnerable to degenerative insults induced by the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor blocker, ketamine. As H19-7 hippocampal progenitor cells isolated from E17 do not express the PMCA2 isoform, they constitute a valuable model for studying its role in neuronal development. In this study, we demonstrated that heterologous expression of PMCA2b enhanced the differentiation of H19-7 cells and protected from ketamine-induced death. PMCA2b did not affect resting [Ca2+]c in the presence or absence of ketamine and had no effect on the rate of Ca2+ clearance following membrane depolarization in the presence of the drug. The upregulation of endogenous PMCA1 demonstrated in response to PMCA2b expression as well as ketamine-induced PMCA4 depletion were indifferent to the rate of Ca2+ clearance in the presence of ketamine. Yet, co-expression of PMCA4b and PMCA2b was able to partially restore Ca2+ extrusion diminished by ketamine. The profiling of NMDA receptor expression showed upregulation of the NMDAR1 subunit in PMCA2b-expressing cells and increased co-immunoprecipitation of both proteins following ketamine treatment. Further microarray screening demonstrated a significant influence of PMCA2b on GABA signaling in differentiating progenitor cells, manifested by the unique regulation of several genes key to the GABAergic transmission. The overall activity of glutamate decarboxylase remained unchanged, but Ca2+-induced GABA release was inhibited in the presence of ketamine. Interestingly, PMCA2b expression was able to reverse this effect. The mechanism of GABA secretion normalization in the presence of ketamine may involve PMCA2b-mediated inhibition of GABA transaminase, thus shifting GABA utilization from energetic purposes to neurosecretion. In this study, we show for the first time that developmentally controlled PMCA expression may dictate the pattern of differentiation of hippocampal progenitor cells. Moreover, the appearance of PMCA2 early in development has long-standing consequences for GABA metabolism with yet an unpredictable influence on GABAergic neurotransmission during later stages of brain maturation. In contrast, the presence of PMCA2b seems to be protective for differentiating progenitor cells from ketamine-induced apoptotic death.
Keywords: GABA metabolism; calcium; hippocampal progenitor cells; ketamine; neuronal differentiation; plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA).
Copyright © 2022 Lisek, Mackiewicz, Sobolczyk, Ferenc, Guo, Zylinska and Boczek.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 2b interacts preferentially with Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 2 in apical plasma membranes.J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 22;277(12):10506-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111616200. Epub 2002 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11786550
-
Glutamate Deregulation in Ketamine-Induced Psychosis-A Potential Role of PSD95, NMDA Receptor and PMCA Interaction.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jun 28;11:181. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00181. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28701926 Free PMC article.
-
Region-specific effects of repeated ketamine administration on the presynaptic GABAergic neurochemistry in rat brain.Neurochem Int. 2015 Dec;91:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Neurochem Int. 2015. PMID: 26492822
-
Fast-acting antidepressant activity of ketamine: highlights on brain serotonin, glutamate, and GABA neurotransmission in preclinical studies.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jul;199:58-90. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.02.017. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30851296 Review.
-
GABAergic deafferentation hypothesis of brain aging and Alzheimer's disease revisited.Brain Res Bull. 1998;45(4):341-79. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(97)00347-x. Brain Res Bull. 1998. PMID: 9527011 Review.
References
-
- Abekawa T., Ito K., Nakagawa S., Koyama T. (2007). Prenatal EXPOSURE to an NMDA Receptor antagonist, MK-801 reduces density of parvalbumin-immunoreactive GABAergic neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex and enhances phencyclidine-induced hyperlocomotion but not behavioral sensitization to methamphetamine in postpubertal rats. Psychopharmacology 192, 303–316. 10.1007/s00213-007-0729-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

