Characterization of a Deep-Sea Actinobacterium Strain Uncovers Its Prominent Capability of Utilizing Taurine and Polyvinyl Alcohol
- PMID: 35677903
- PMCID: PMC9169050
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.868728
Characterization of a Deep-Sea Actinobacterium Strain Uncovers Its Prominent Capability of Utilizing Taurine and Polyvinyl Alcohol
Abstract
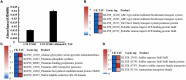
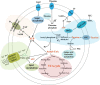
Actinobacteria represent a large group of important prokaryotes with great application potentials and widely distribute in diverse natural environments including the ocean. However, compared to their terrestrial cultured members, there are much less available marine Actinobacteria, especially deep-sea counterparts. Here, we cultured a bacterial strain of deep-sea actinobacterium, Marmoricola sp. TYQ2, by using a basal medium supplemented with taurine. Consistently, the growth of strain TYQ2 was significantly promoted by the supplement of taurine. Transcriptomic analysis showed that the expressions of genes encoding proteins associated with taurine metabolization and utilization as well as energy generation were evidently up-regulated when taurine was added. Moreover, strain TYQ2 was demonstrated to degrade polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with the involvement of the redox cycle of extracellular quinol and quinone and the reduction of iron to ferrous, and strain TYQ2 could utilize the degradation products for energy production, thereby supporting bacterial growth. Overall, our experimental results demonstrate the prominent degradation capabilities of Marmoricola sp. TYQ2 toward the organics taurine and PVA.
Keywords: actinomyces; cultivation; deep sea; polyvinyl alcohol; taurine.
Copyright © 2022 Tan, Shan, Zheng, Liu and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

