Emergence of a High-Risk Klebsiella michiganensis Clone Disseminating Carbapenemase Genes
- PMID: 35677907
- PMCID: PMC9169563
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.880248
Emergence of a High-Risk Klebsiella michiganensis Clone Disseminating Carbapenemase Genes
Abstract
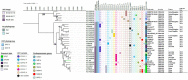
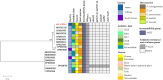
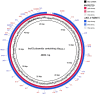
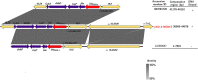
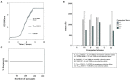
Klebsiella michiganensis is emerging as an important human pathogen of concern especially strains with plasmid-mediated carbapenemase genes. The IncX3-bla NDM-5 plasmid has been described as the primary vector for bla NDM-5 dissemination. However, whether strains with this plasmid have any competitive edge remain largely unexplored. We characterized a bla NDM-5-producing Klebsiella michiganensis strain (KO_408) from Japan and sought to understand the driving force behind the recent dissemination of IncX3-blaNDM-5 plasmids in different bacterial hosts. Antibiotic susceptibility testing, conjugation, and whole-genome sequencing were performed for KO_408, a clinical isolate recovered from a respiratory culture. Fitness, stability, and competitive assays were performed using the IncX3-bla NDM-5 plasmid, pKO_4-NDM-5. KO_408 was ascribed to a novel sequence type, ST256, and harbored resistance genes conforming to its MDR phenotype. The bla NDM-5 gene was localized on the ~44.9 kb IncX3 plasmid (pKO_4-NDM-5), which was transferable in the conjugal assay. The acquisition of pKO_4-NDM-5 did not impose any fitness burden and showed high stability in the host cells. However, transformants with pKO_4-NDM-5 were outcompeted by their host cells and transconjugants with the IncX3-bla OXA-181 plasmid. The genetic environment of bla NDM-5 in pKO_4-NDM-5 has been previously described. pKO_4-NDM-5 showed a close phylogenetic distance with seven similar plasmids from China. KO_408 clustered with strains within the KoI phylogroup, which is closely associated with carbapenemase genes. This study highlights the emergence of a high-risk Klebsiella michiganensis clone harboring carbapenemase genes and affirms that the recent spread of IncX3-bla NDM-5 plasmids might be due to their low fitness cost and stability but not their competitive prowess.
Keywords: IncX3-blaNDM-5 plasmid; Klebsiella michiganensis; KoI; fitness cost; stability.
Copyright © 2022 Prah, Nukui, Yamaoka and Saito.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chapman P., Forde B. M., Roberts L. W., Bergh H., Vesey D., Jennison A. V., et al. . (2020). Genomic investigation reveals contaminated detergent as the source of an extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella michiganensis outbreak in a neonatal unit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58:e01980-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01980-19, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

