Evaluation of Serum Ferritin, Procalcitonin, and C-Reactive Protein for the Prediction of Severity and Mortality in Hemorrhagic Fever With Renal Syndrome
- PMID: 35677912
- PMCID: PMC9169039
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.865233
Evaluation of Serum Ferritin, Procalcitonin, and C-Reactive Protein for the Prediction of Severity and Mortality in Hemorrhagic Fever With Renal Syndrome
Abstract
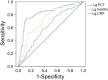
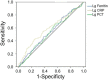
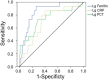
This study aimed to analyze the clinical significance of serum ferritin, procalcitonin (PCT), and C-reactive protein (CRP) in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). The demographical, clinical, and laboratory data of 373 patients with HFRS in northeastern China were retrospectively analyzed. The levels of serum ferritin and PCT in severe patients (n = 108) were significantly higher than those in mild patients (n = 265, p < 0.001) and associated with HFRS severity. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values of serum ferritin and PCT for predicting the severity of HFRS were 0.732 (95% CI 0.678-0.786, p < 0.001) and 0.824 (95% CI 0.773-0.875, p < 0.001), respectively, showing sensitivity and specificity of 0.75 and 0.88 for serum ferritin, and 0.76 and 0.60 for PCT. The CRP level in HFRS with bacterial co-infection (n = 115) was higher than that without bacterial co-infection (n = 258, p < 0.001). The AUC value of CRP for predicting bacterial co-infection was 0.588 (95% CI 0.525-0.652, p < 0.001), showing sensitivity and specificity of 0.43 and 0.76, respectively. The serum ferritin level in non-survivors (n = 14) was significantly higher than in survivors (n = 359, p < 0.001). The AUC value of serum ferritin for predicting mortality was 0.853 (95% CI 0.774-0.933, p < 0.001), showing sensitivity and specificity of 0.933 and 0.739. Serum ferritin and PCT have a robust association with HFRS severity and mortality, which may be promising predictors, and CRP is an effective biomarker to assess bacterial co-infection in HFRS.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; hantaviruses; hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; procalcitonin; serum ferritin.
Copyright © 2022 Che, Wang, Du, Li, Zhao, Zhang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cooper I. D., Crofts C. A. P., DiNicolantonio J. J., Malhotra A., Elliott B., Kyriakidou Y., et al. (2020). Relationships between hyperinsulinaemia, magnesium, vitamin D, thrombosis and COVID-19: rationale for clinical management. Open Heart 7:e001356. 10.1136/openhrt-2020-001356 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

