Genetic polymorphism in Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase chloride transport protein 6 (MTHFR CLCN6) gene is associated with keratinocyte skin cancer in a cohort of renal transplant recipients
- PMID: 35677930
- PMCID: PMC9168012
- DOI: 10.1002/ski2.95
Genetic polymorphism in Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase chloride transport protein 6 (MTHFR CLCN6) gene is associated with keratinocyte skin cancer in a cohort of renal transplant recipients
Abstract
Background: Renal transplant recipients (RTRs) are at increased risk of keratinocyte cancer (KC), especially cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). Previous studies identified a genetic variant of the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) gene, C677T, which conferred a risk for diagnosis of cSCC in Irish RTRs.
Objective: We sought to find further genetic variation in MTHFR and overlap genes that may be associated with a diagnosis of KC in RTRs.
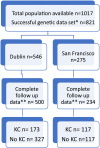
Methods: Genotyping of a combined RTR population (n = 821) from two centres, Ireland (n = 546) and the USA (n = 275), was performed. This included 290 RTRs with KC and 444 without. Eleven single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the MTHFR gene and seven in the overlap gene MTHFR Chloride transport protein 6 (CLCN6) were evaluated and association explored by time to event analysis (from transplant to first KC) using Cox proportional hazards model.
Results: Polymorphism at MTHFR CLCN6 (rs9651118) was significantly associated with KC in RTRs (HR 1.50, 95% CI 1.17-1.91, p < 0.00061) and cSCC (HR 1.63, 95% CI 1.14-2.34, p = 0.007). A separate SNP, MTHFR C677T, was also significantly associated with KC in the Irish population (HR 1.31, 95% CI 1.05-1.63, p = 0.016), but not American RTRs.
Conclusions: We report the association of a SNP in the MTHFR overlap gene, CLCN6 and KC in a combined RTR population. While the exact function of CLCN6 is not known, it is proposed to be involved in folate availability. Future applications could include incorporation in a polygenic risk score for KC in RTRs to help identify those at increased risk beyond traditional risk factor assessment.
© 2022 The Authors. Skin Health and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- van Doorn R, Gruis NA, Willemze R, van der Velden PA, Tensen CP. Aberrant DNA methylation in cutaneous malignancies. Semin Oncol. 2005;32(5):479–87. - PubMed
-
- Laing ME, Dicker P, Moloney FJ, Ho WL, Murphy GM, Conlon P, et al. Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism and the risk of squamous cell carcinoma in renal transplant patients. Transplantation. 2007;84(1):113–6. - PubMed
-
- Laing ME, Cummins R, O’Grady A, O’Kelly P, Kay EW, Murphy GM. Aberrant DNA methylation associated with MTHFR C677T genetic polymorphism in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in renal transplant patients. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163(2):345–52. - PubMed
-
- Moloney FJ, Comber H, O’Lorcain P, O’Kelly P, Conlon PJ, Murphy GM. A population‐based study of skin cancer incidence and prevalence in renal transplant recipients. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154(3):498–504. - PubMed
-
- Martinez J‐C, Otley CC, Stasko T, Euvrard S, Brown C, Schanbacher CF, et al. Defining the clinical course of metastatic skin cancer in organ transplant recipients: a multicenter collaborative study. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(3):301–6. - PubMed