Non-PCR Ultrasensitive Detection of Viral RNA by a Nanoprobe-Coupling Strategy: SARS-CoV-2 as an Example
- PMID: 35678310
- PMCID: PMC9347949
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202200031
Non-PCR Ultrasensitive Detection of Viral RNA by a Nanoprobe-Coupling Strategy: SARS-CoV-2 as an Example
Abstract
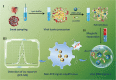
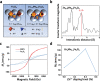
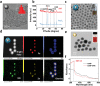
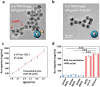
Developing efficient and highly sensitive diagnostic techniques for early detections of pathogenic viruses such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is vitally important for preventing its widespread. However, the conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based detection features high complexity, excessive time-consumption, and labor-intensiveness, while viral protein-based detections suffer from moderate sensitivity and specificity. Here, a non-PCR but ultrasensitive viral RNA detection strategy is reported based on a facile nanoprobe-coupling strategy without enzymatic amplification, wherein PCR-induced bias and other shortcomings are successfully circumvented. This approach endows the viral RNA detection with ultra-low background to maximum signal ratio in the linear signal amplification by using Au nanoparticles as reporters. The present strategy exhibits 100% specificity toward SARS-CoV-2 N gene, and ultrasensitive detection of as low as 52 cp mL-1 of SARS-CoV-2 N gene without pre-PCR amplification. This approach presents a novel ultrasensitive tool for viral RNA detections for fighting against COVID-19 and other types of pathogenic virus-caused diseases.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 N gene; Zn2+ doping; magnetic nanoparticles; nanoprobe-coupling strategy; nucleic acid quick detection.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- a) Li Z. T., Yi Y. X., Luo X. M., Xiong N., Liu Y., Li S. Q., Sun R. L., Wang Y. Q., Hu B. C., Chen W., Zhang Y. C., Wang J., Huang B. F., Lin Y., Yang J. S., Cai W. S., Wang X. F., Cheng J., Chen Z. Q., Sun K. J., Pan W. M., Zhan Z. F., Chen L. Y., Ye F., J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1518; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Sun M., Liu S., Wei X., Wan S., Huang M., Song T., Lu Y., Weng X., Lin Z., Chen H., Song Y., Yang C., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 10266. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xiong E., Jiang L., Tian T., Hu M., Yue H., Huang M., Lin W., Jiang Y., Zhu D., Zhou X., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5307. - PubMed
-
- Zainol Rashid Z., Othman S. N., Abdul Samat M. N., Ali U. K., Wong K. K., Malays. J. Pathol. 2020, 42, 13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

