Aberrant Nuclear Translocation of E2F1 and Its Association in Cushing's Disease
- PMID: 35678423
- PMCID: PMC9246279
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqac086
Aberrant Nuclear Translocation of E2F1 and Its Association in Cushing's Disease
Abstract
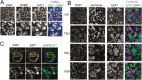
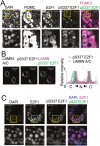
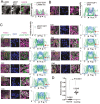
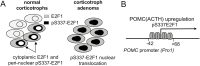
Nonsurgical medical treatments are often performed for Cushing's disease due to high recurrence rates. However, current medical treatment that targets corticotroph adenomas are limited. To develop a treatment that specifically targets corticotrophs in Cushing's disease, it is necessary to identify corticotroph lineage-specific proteins, which are involved in the Cushing's tumor phenotype. We have previously reported that the expression of E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1), one of the cell cycle regulatory proteins, was increased in corticotrophs in Cushing's disease model mice and was involved in the regulation of POMC gene expression. Phosphorylation of Ser337 of E2F1 (pS337-E2F1) facilitates its binding to the POMC promoter, which was suggested to contribute to elevated POMC expression in corticotrophs. Here, we report that E2F1 expression is specific to the corticotroph lineage in normal human pituitaries and that the E2F1 protein is localized in the cytosol in normal corticotrophs. We show that pS337-E2F1 is localized in the nucleus specifically in Cushing's tumors, while it is localized in the perinuclear cytoplasm in the normal pituitary. This observation demonstrates that pS337 is a marker for Cushing's tumors and suggests that phosphorylation of E2F1 may be a target for developing a novel pharmacological treatment for tumorigenesis and hormone dysregulation of Cushing's disease.
Keywords: Cushing’s disease; E2F1; POMC; corticotroph; pS337-E2F1.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is E2F1 a Potential Medical Therapy Target for Cushing Disease?Endocrinology. 2022 Sep 1;163(9):bqac117. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqac117. Endocrinology. 2022. PMID: 35876125 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
E2F1-mediated human POMC expression in ectopic Cushing's syndrome.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016 Nov;23(11):857-870. doi: 10.1530/ERC-16-0206. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27935805 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of SOM230 on adrenocorticotropic hormone production and corticotroph tumor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Aug 25;394(1-2):37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25011056
-
Targeting the ERK pathway for the treatment of Cushing's disease.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):69149-69158. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12381. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27708250 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in Cushing's disease.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 May 14;286(1-2):199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.10.015. Epub 2007 Nov 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18221833 Review.
-
The role of somatostatin analogs in Cushing's disease.Pituitary. 2004;7(4):257-64. doi: 10.1007/s11102-005-1404-x. Pituitary. 2004. PMID: 16132202 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogeneity of TPIT expression in ACTH-secreting extra-pituitary neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) supports the existence of different cellular programs in pancreatic and pulmonary NETs.Virchows Arch. 2023 Nov;483(5):635-643. doi: 10.1007/s00428-023-03642-2. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Virchows Arch. 2023. PMID: 37726450
-
Genetic models of Cushing's disease : From cells, in vivo transgenic models to human pituitary organoids.Pituitary. 2025 Apr 5;28(2):47. doi: 10.1007/s11102-025-01516-1. Pituitary. 2025. PMID: 40186634 Review.
References
-
- Pivonello R, Fleseriu M, Newell-Price J, et al. . Efficacy and safety of osilodrostat in patients with Cushing’s disease (LINC 3): a multicentre phase III study with a double-blind, randomised withdrawal phase. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(9):748-761. Doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30240-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castinetti F, Morange I, Jaquet P, Conte-Devolx B, Brue T. Ketoconazole revisited: a preoperative or postoperative treatment in Cushing’s disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;158(1):91-99. - PubMed
-
- Ferriere A, Cortet C, Chanson P, et al. . Cabergoline for Cushing’s disease: a large retrospective multicenter study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2017;176(3):305-314. - PubMed
-
- Colao A, Petersenn S, Newell-Price J, et al. . A 12-month phase 3 study of pasireotide in Cushing’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(10):914-924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

