The sRNA NsiR4 fine-tunes arginine synthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 by post-transcriptional regulation of PirA
- PMID: 35678613
- PMCID: PMC9196836
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2082147
The sRNA NsiR4 fine-tunes arginine synthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 by post-transcriptional regulation of PirA
Abstract
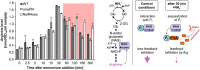
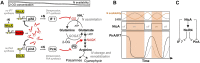
As the only oxygenic phototrophs among prokaryotes, cyanobacteria employ intricate mechanisms to regulate common metabolic pathways. These mechanisms include small protein inhibitors exerting their function by protein-protein interaction with key metabolic enzymes and regulatory small RNAs (sRNAs). Here we show that the sRNA NsiR4, which is highly expressed under nitrogen limiting conditions, interacts with the mRNA of the recently described small protein PirA in the model strain Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. In particular, NsiR4 targets the pirA 5'UTR close to the ribosome binding site. Heterologous reporter assays confirmed that this interaction interferes with pirA translation. PirA negatively impacts arginine synthesis under ammonium excess by competing with the central carbon/nitrogen regulator PII that binds to and thereby activates the key enzyme of arginine synthesis, N-acetyl-L-glutamate-kinase (NAGK). Consistently, ectopic nsiR4 expression in Synechocystis resulted in lowered PirA accumulation in response to ammonium upshifts, which also affected intracellular arginine pools. As NsiR4 and PirA are inversely regulated by the global nitrogen transcriptional regulator NtcA, this regulatory axis enables fine tuning of arginine synthesis and conveys additional metabolic flexibility under highly fluctuating nitrogen regimes. Pairs of small protein inhibitors and of sRNAs that control the abundance of these enzyme effectors at the post-transcriptional level appear as fundamental building blocks in the regulation of primary metabolism in cyanobacteria.
Keywords: Cyanobacteria; RNA regulator; arginine metabolism; nitrogen assimilation; posttranscriptional regulation; sRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Novel PII-Interacting Protein PirA Controls Flux into the Cyanobacterial Ornithine-Ammonia Cycle.mBio. 2021 Mar 23;12(2):e00229-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00229-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33758091 Free PMC article.
-
The sRNA NsiR4 is involved in nitrogen assimilation control in cyanobacteria by targeting glutamine synthetase inactivating factor IF7.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 10;112(45):E6243-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508412112. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26494284 Free PMC article.
-
A nitrogen stress-inducible small RNA regulates CO2 fixation in Nostoc.Plant Physiol. 2021 Oct 5;187(2):787-798. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab309. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34608966 Free PMC article.
-
The PII-NAGK-PipX-NtcA Regulatory Axis of Cyanobacteria: A Tale of Changing Partners, Allosteric Effectors and Non-covalent Interactions.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Nov 13;5:91. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00091. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30483512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ammonium assimilation in cyanobacteria.Photosynth Res. 2005;83(2):135-50. doi: 10.1007/s11120-004-2082-7. Photosynth Res. 2005. PMID: 16143848 Review.
Cited by
-
How Small Proteins Adjust the Metabolism of Cyanobacteria Under Stress: The Role of Small Proteins in Cyanobacterial Stress Responses.Bioessays. 2025 Mar;47(3):e202400245. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400245. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39668401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactors and effects of overexpressing YlxR/RnpM, a conserved RNA binding protein in cyanobacteria.RNA Biol. 2024 Jan;21(1):1-19. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2429230. Epub 2024 Dec 3. RNA Biol. 2024. PMID: 39625117 Free PMC article.
-
Protein NirP1 regulates nitrite reductase and nitrite excretion in cyanobacteria.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 1;15(1):1911. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46253-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38429292 Free PMC article.
-
What determines symbiotic nitrogen fixation efficiency in rhizobium: recent insights into Rhizobium leguminosarum.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Aug 5;205(9):300. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03640-7. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37542687 Review.
References
-
- Forchhammer K. Glutamine signalling in bacteria. Front Biosci J Virtual Libr. 2007;12(1):358–370. - PubMed
-
- Stadtman ER. The story of glutamine synthetase regulation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(48):44357–44364. - PubMed
-
- Mangum JH, Magni G, Stadtman ER. Regulation of glutamine synthetase adenylylation and deadenylylation by the enzymatic uridylylation and deuridylylation of the PII regulatory protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973;158(2):514–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
