Discriminatory Gleason grade group signatures of prostate cancer: An application of machine learning methods
- PMID: 35679280
- PMCID: PMC9182297
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267714
Discriminatory Gleason grade group signatures of prostate cancer: An application of machine learning methods
Abstract
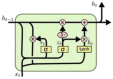
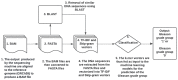
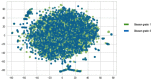
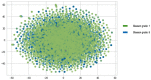
One of the most precise methods to detect prostate cancer is by evaluation of a stained biopsy by a pathologist under a microscope. Regions of the tissue are assessed and graded according to the observed histological pattern. However, this is not only laborious, but also relies on the experience of the pathologist and tends to suffer from the lack of reproducibility of biopsy outcomes across pathologists. As a result, computational approaches are being sought and machine learning has been gaining momentum in the prediction of the Gleason grade group. To date, machine learning literature has addressed this problem by using features from magnetic resonance imaging images, whole slide images, tissue microarrays, gene expression data, and clinical features. However, there is a gap with regards to predicting the Gleason grade group using DNA sequences as the only input source to the machine learning models. In this work, using whole genome sequence data from South African prostate cancer patients, an application of machine learning and biological experiments were combined to understand the challenges that are associated with the prediction of the Gleason grade group. A series of machine learning binary classifiers (XGBoost, LSTM, GRU, LR, RF) were created only relying on DNA sequences input features. All the models were not able to adequately discriminate between the DNA sequences of the studied Gleason grade groups (Gleason grade group 1 and 5). However, the models were further evaluated in the prediction of tumor DNA sequences from matched-normal DNA sequences, given DNA sequences as the only input source. In this new problem, the models performed acceptably better than before with the XGBoost model achieving the highest accuracy of 74 ± 01, F1 score of 79 ± 01, recall of 99 ± 0.0, and precision of 66 ± 0.1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Cassim N, Ahmad A, Wadee R, Rebbeck T, Glencross D, George J. Prostate cancer age-standardised incidence increase between 2006 and 2016 in Gauteng Province, South Africa: A laboratory data-based analysis. South African Medical Journal. 2021;111(1):26–32. doi: 10.7196/SAMJ.2020.v111i1.14850 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, et al.. Guidelines on prostate cancer. European association of urology. 2012; p. 45. - PubMed
-
- van der Leest M, Cornel E, Israël B, Hendriks R, Padhani AR, Hoogenboom M, et al.. Head-to-head comparison of transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy versus multiparametric prostate resonance imaging with subsequent magnetic resonance-guided biopsy in biopsy-naive men with elevated prostate-specific antigen: a large prospective multicenter clinical study. European urology. 2019;75(4):570–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

