Lysosome lipid signalling from the periphery to neurons regulates longevity
- PMID: 35681008
- PMCID: PMC9203275
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-022-00926-8
Lysosome lipid signalling from the periphery to neurons regulates longevity
Abstract
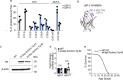
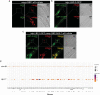
Lysosomes are key cellular organelles that metabolize extra- and intracellular substrates. Alterations in lysosomal metabolism are implicated in ageing-associated metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. However, how lysosomal metabolism actively coordinates the metabolic and nervous systems to regulate ageing remains unclear. Here we report a fat-to-neuron lipid signalling pathway induced by lysosomal metabolism and its longevity-promoting role in Caenorhabditis elegans. We discovered that induced lysosomal lipolysis in peripheral fat storage tissue upregulates the neuropeptide signalling pathway in the nervous system to promote longevity. This cell-non-autonomous regulation is mediated by a specific polyunsaturated fatty acid, dihomo-γ-linolenic acid, and LBP-3 lipid chaperone protein transported from the fat storage tissue to neurons. LBP-3 binds to dihomo-γ-linolenic acid, and acts through NHR-49 nuclear receptor and NLP-11 neuropeptide in neurons to extend lifespan. These results reveal lysosomes as a signalling hub to coordinate metabolism and ageing, and lysosomal signalling mediated inter-tissue communication in promoting longevity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.W. is a cofounder of Chemical Biology Probes LLC and Coactigon Inc. The focuses of these companies are unrelated to this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







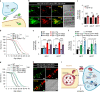


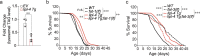
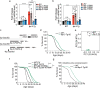

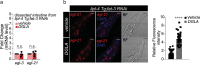
Comment in
-
Long life depends on open communication.Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Jun;24(6):808-810. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00908-w. Nat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35681007 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HG011633/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG066606/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG062257/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044346/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG045183/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008602/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074540/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA262623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- RF1 AG074540/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES027801/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DK113644/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT009050/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG070417/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

