The impact of intraoperative radiotherapy on breast cancer: focus on the levels of angiogenic factors
- PMID: 35681234
- PMCID: PMC9178821
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02653-8
The impact of intraoperative radiotherapy on breast cancer: focus on the levels of angiogenic factors
Abstract
Objective: Angiogenesis is one of the hallmarks of cancers that is involved in tumor progression. Angiogenic factors induce the formation of new blood vessels and tumor extension, and finally reduce the survival of patients. Intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT), in which radiation is delivered to the tumor bed can kill cells and change tumor microenvironment. Here, we compared the impact of IORT on the levels of angiogenic factors in the blood and surgical wound fluids (SWF) of the breast cancer patients.
Patients and methods: Three hundred sixty patients, who had undergone breast-conserving surgery between 2013 and 2018, were enrolled in IORT and non-IORT groups non-randomly. Blood and drained wound fluid (WF) samples were collected from the patients before and after surgery, followed by quantification of the amounts of TGF-β, EGF, FGF, VEGF, and DLL4 in the patients using ELISA.
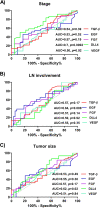
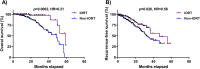
Results: Our results were indicative of significant differences between the pre-surgery and post-surgery serum levels of EGF, DLL4, and VEGF. Furthermore, ROC analyses showed that TGF-β and DLL4 can differentiate of the early-stage from late-stage of the disease. Interestingly, the rate of the death and recurrence was reduced in IORT group.
Conclusions: In summary, IORT is a safe and effective treatment that can affect angiogenic factors and improve the overall- and recurrence-free survival of breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DLL4; EGF; FGF; IORT; TGF-β; VEGF.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Baharlou R, Atashzar MR, Vasmehjani AA, Rahimi E, Khoshmirsafa M, Seif F, Mahdiyar M. Reduced levels of T-helper 17-associated cytokines in the serum of patients with breast cancer: indicators for following the course of disease. Central Eur J Immunol. 2016;41:78. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2016.58819. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bray Freddie, Ferlay Jacques, Soerjomataram Isabelle, Siegel Rebecca L., Torre Lindsey A., Jemal Ahmedin. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baharlou R, Tajik N, Behdani M, Shokrgozar MA, Tavana V, Kazemi-Lomedasht F, Faraji F, Habibi-Anbouhi M. An antibody fragment against human delta-like ligand-4 for inhibition of cell proliferation and neovascularization. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018;40:368–374. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2018.1505907. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

