Pulsed Electric Field: Fundamentals and Effects on the Structural and Techno-Functional Properties of Dairy and Plant Proteins
- PMID: 35681305
- PMCID: PMC9180040
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11111556
Pulsed Electric Field: Fundamentals and Effects on the Structural and Techno-Functional Properties of Dairy and Plant Proteins
Abstract
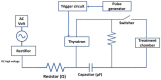
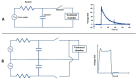
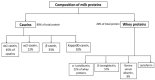
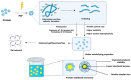
Dairy and plant-based proteins are widely utilized in various food applications. Several techniques have been employed to improve the techno-functional properties of these proteins. Among them, pulsed electric field (PEF) technology has recently attracted considerable attention as a green technology to enhance the functional properties of food proteins. In this review, we briefly explain the fundamentals of PEF devices, their components, and pulse generation and discuss the impacts of PEF treatment on the structure of dairy and plant proteins. In addition, we cover the PEF-induced changes in the techno-functional properties of proteins (including solubility, gelling, emulsifying, and foaming properties). In this work, we also discuss the main challenges and the possible future trends of PEF applications in the food proteins industry. PEF treatments at high strengths could change the structure of proteins. The PEF treatment conditions markedly affect the treatment results with respect to proteins' structure and techno-functional properties. Moreover, increasing the electric field strength could enhance the emulsifying properties of proteins and protein-polysaccharide complexes. However, more research and academia-industry collaboration are recommended to build highly effective PEF devices with controlled processing conditions.
Keywords: functional properties; milk proteins; plant proteins; protein structure; pulse generation; pulsed electric field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tailoring the Techno-Functional Properties of Fava Bean Protein Isolates: A Comparative Evaluation of Ultrasonication and Pulsed Electric Field Treatments.Foods. 2024 Jan 24;13(3):376. doi: 10.3390/foods13030376. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338512 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Pulsed Electric Field on the Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Micellar Casein.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;15(15):3311. doi: 10.3390/polym15153311. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571205 Free PMC article.
-
Techno-functional properties of dry-fractionated plant-based proteins and application in food product development: a review.J Sci Food Agric. 2024 Mar 15;104(4):1884-1896. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13168. Epub 2023 Dec 9. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. PMID: 38009309 Review.
-
Current and future prospects for the use of pulsed electric field in the meat industry.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(10):1660-1674. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1425825. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 29393666 Review.
-
The forgotten method? Pulsed electric field thresholds from the perspective of texture analysis.Food Res Int. 2024 Jan;176:113869. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113869. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38163693
Cited by
-
Combination of Milk and Plant Proteins to Develop Novel Food Systems: What Are the Limits?Foods. 2023 Jun 15;12(12):2385. doi: 10.3390/foods12122385. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37372596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modification of plant proteins as alternatives to animal proteins: a review.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 24;34(2):349-363. doi: 10.1007/s10068-024-01705-x. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39944661 Review.
-
Developments in Plant Proteins Production for Meat and Fish Analogues.Molecules. 2023 Mar 27;28(7):2966. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072966. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulsed Electric Field Pretreatment Enhances the Enzyme Hydrolysis of Baker's Yeast.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 1;12(12):2470. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122470. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770673 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring the Techno-Functional Properties of Fava Bean Protein Isolates: A Comparative Evaluation of Ultrasonication and Pulsed Electric Field Treatments.Foods. 2024 Jan 24;13(3):376. doi: 10.3390/foods13030376. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jambrak A.R., Mason T.J., Lelas V., Herceg Z., Herceg I.L. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Solubility and Foaming Properties of Whey Protein Suspensions. J. Food Eng. 2008;86:281–287. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.10.004. - DOI
-
- European Comission Milk Market Observatory. 2020. [(accessed on 21 December 2020)]. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/food-farming-fisheries/farming/facts-and-figur....
-
- Nunes L., Tavares G.M. Thermal Treatments and Emerging Technologies: Impacts on the Structure and Techno-Functional Properties of Milk Proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;90:88–99. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.06.004. - DOI
-
- Han Z., Cai M.J., Cheng J.H., Sun D.W. Effects of Electric Fields and Electromagnetic Wave on Food Protein Structure and Functionality: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;75:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.02.017. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

