Hu Antigen R (HuR) Protein Structure, Function and Regulation in Hepatobiliary Tumors
- PMID: 35681645
- PMCID: PMC9179498
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14112666
Hu Antigen R (HuR) Protein Structure, Function and Regulation in Hepatobiliary Tumors
Abstract
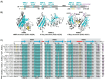
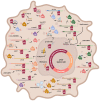
Hu antigen R (HuR) is a 36-kDa ubiquitous member of the ELAV/Hu family of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), which plays an important role as a post-transcriptional regulator of specific RNAs under physiological and pathological conditions, including cancer. Herein, we review HuR protein structure, function, and its regulation, as well as its implications in the pathogenesis, progression, and treatment of hepatobiliary cancers. In particular, we focus on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), tumors where the increased cytoplasmic localization of HuR and activity are proposed, as valuable diagnostic and prognostic markers. An overview of the main regulatory axes involving HuR, which are associated with cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, apoptosis, and autophagy in HCC, is provided. These include the transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational modulators of HuR function, in addition to HuR target transcripts. Finally, whereas studies addressing the relevance of targeting HuR in CCA are limited, in the past few years, HuR has emerged as a potential therapeutic target in HCC. In fact, the therapeutic efficacy of some pharmacological inhibitors of HuR has been evaluated, in early experimental models of HCC. We, further, discuss the major findings and future perspectives of therapeutic approaches that specifically block HuR interactions, either with post-translational modifiers or cognate transcripts in hepatobiliary cancers.
Keywords: ELAV-like protein 1; RNA-binding protein; cholangiocarcinoma; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUMOylation controls Hu antigen R posttranscriptional activity in liver cancer.Cell Rep. 2024 Mar 26;43(3):113924. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113924. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38507413 Free PMC article.
-
HuR Protein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Development, Prognosis and Treatment.Biomedicines. 2021 Jan 27;9(2):119. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020119. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33513829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hu antigen R (HuR) is a positive regulator of the RNA-binding proteins TDP-43 and FUS/TLS: implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 14;289(46):31792-31804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.573246. Epub 2014 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25239623 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding and targeting the disease-related RNA binding protein human antigen R (HuR).Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020 May;11(3):e1581. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1581. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020. PMID: 31970930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple functions of the RNA-binding protein HuR in cancer progression, treatment responses and prognosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 10;14(5):10015-41. doi: 10.3390/ijms140510015. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23665903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal AFAP1-AS1 Promotes the Growth, Metastasis, and Glycolysis of Pituitary Adenoma by Inhibiting HuR Degradation.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):2212-2229. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04387-y. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39090353 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Human Antigen R (HuR): A Key Player in Liver Metabolism and MASLD.Livers. 2025 Sep;5(3):33. doi: 10.3390/livers5030033. Epub 2025 Jul 21. Livers. 2025. PMID: 40809813 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Role of RNA-Binding Proteins, with a Focus on RPS5, in the Malignant Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 7;25(2):773. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020773. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255847 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation controls Hu antigen R posttranscriptional activity in liver cancer.Cell Rep. 2024 Mar 26;43(3):113924. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113924. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38507413 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Synergistic Supplementation of NAD+ Promoting Compounds as a Strategy for Increasing Healthspan.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 14;15(2):445. doi: 10.3390/nu15020445. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- RTC2019-007125-1/Programa Retos-Colaboración
- DTS20/00138/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PID2020-117116RB-I00, PGC2018-096049-B-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (MICINN), integrated in the Plan Estatal de Investigación Científica y Técnica e Innovación
- BIO-198, US-1254317, US-1257019, P18-FR-3487, P18-HO-4091/Gobierno de Andalucía
- HR17-00601/La Caixa Foundation Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

