Use of Glycoproteins-Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen and Galectin-3 as Primary Tumor Markers and Therapeutic Targets in the Management of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 35681683
- PMCID: PMC9179331
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14112704
Use of Glycoproteins-Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen and Galectin-3 as Primary Tumor Markers and Therapeutic Targets in the Management of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Abstract
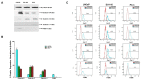
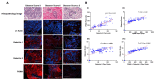
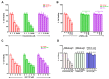
Galectins and prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) are glycoproteins that are functionally implicated in prostate cancer (CaP). We undertook this study to analyze the "PSMA-galectin pattern" of the human CaP microenvironment with the overarching goal of selecting novel-molecular targets for prognostic and therapeutic purposes. We examined CaP cells and biopsy samples representing different stages of the disease and found that PSMA, Gal-1, Gal-3, and Gal-8 are the most abundantly expressed glycoproteins. In contrast, other galectins such as Gal-2, 4-7, 9-13, were uniformly expressed at lower levels across all cell lines. However, biopsy samples showed markedly higher expression of PSMA, Gal-1 and Gal-3. Independently PSA and Gleason score at diagnosis correlated with the expression of PSMA, Gal-3. Additionally, the combined index of PSMA and Gal-3 expression positively correlated with Gleason score and was a better predictor of tumor aggressiveness. Together, our results recognize a tightly regulated "PSMA-galectin- pattern" that accompanies disease in CaP and highlight a major role for the combined PSMA and Gal-3 inhibitors along with standard chemotherapy for prostate cancer treatment. Inhibitor combination studies show enzalutamide (ENZ), 2-phosphonomethyl pentanedioic acid (2-PMPA), and GB1107 as highly cytotoxic for LNCaP and LNCaP-KD cells, while Docetaxel (DOC) + GB1107 show greater efficacy in PC-3 cells. Overall, 2-PMPA and GB1107 demonstrate synergistic cytotoxic effects with ENZ and DOC in various CaP cell lines.
Keywords: galectins; glycoproteins; metastasis; prostate cancer; prostate specific membrane antigen; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pianou N.K., Stavrou P.Z., Vlontzou E., Rondogianni P., Exarhos D.N., Datseris I.E. More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using (18)F-PSMA PET/CT. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2019;22:6–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

