Unraveling the Role of Guanylate-Binding Proteins (GBPs) in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Literature Review and New Data on Prognosis in Breast Cancer Subtypes
- PMID: 35681772
- PMCID: PMC9179834
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14112794
Unraveling the Role of Guanylate-Binding Proteins (GBPs) in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Literature Review and New Data on Prognosis in Breast Cancer Subtypes
Abstract
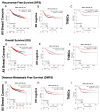
At least one member of the Guanylate-Binding Protein (GBP) family of large interferon-induced GTPases has been classified as both a marker of good prognosis and as a potential drug target to treat breast cancers. However, the activity of individual GBPs appears to not just be tumor cell type-specific but dependent on the growth factor and/or cytokine environment in which the tumor cells reside. To clarify what we do and do not know about GBPs in breast cancer, the current literature on GBP-1, GBP-2, and GBP-5 in breast cancer has been assembled. In addition, we have analyzed the role of each of these GBPs in predicting recurrence-free survival (RFS), overall survival (OS), and distance metastasis-free survival (DMFS) as single gene products in different subtypes of breast cancers. When a large cohort of breast cancers of all types and stages were examined, GBP-1 correlated with poor RFS. However, it was the only GBP to do so. When smaller cohorts of breast cancer subtypes grouped into ER+, ER+/HER2-, and HER2+ tumors were analyzed, none of the GBPs influenced RFS, OS, or DMSF as single agents. The exception is GBP-5, which correlated with improved RFS in HER2+ breast cancers. All three GBPs individually predicted improved RFS, OS, and DMSF in ER- breast cancers, regardless of the PR or HER2 status, and TNBCs.
Keywords: GTPase; distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS); estrogen receptor (ER); guanylate-binding protein (GBP); interferon-γ (IFN-γ); overall survival (OS); progesterone receptor (PR); recurrence-free survival (RFS); signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1); triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The impact of molecular subtype on breast cancer recurrence in young women treated with contemporary adjuvant therapy.Breast J. 2018 Mar;24(2):148-153. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12853. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Breast J. 2018. PMID: 28707744
-
Expression of SIRT1, SIRT3 and SIRT6 Genes for Predicting Survival in Triple-Negative and Hormone Receptor-Positive Subtypes of Breast Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Oct;26(4):2723-2731. doi: 10.1007/s12253-020-00873-5. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 32681437
-
Intracellular trafficking of guanylate-binding proteins is regulated by heterodimerization in a hierarchical manner.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 7;5(12):e14246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014246. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21151871 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of innate immune functions by guanylate-binding proteins.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jan;308(1):237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29174633 Review.
-
The Value of EphB2 Receptor and Cognate Ephrin Ligands in Prognostic and Predictive Assessments of Human Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8098. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158098. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Guanylate binding protein 5 is an immune-related biomarker of oral squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective prognostic study with bioinformatic analysis.Cancer Med. 2024 Jul;13(13):e7431. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7431. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38978333 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between the risk of lymph node metastasis and the expression of GBP1 in breast cancer patients.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(1Part-I):159-164. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.1.8251. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38196488 Free PMC article.
-
A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Sep 18;18(1):20230773. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0773. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37745978 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Roles of Guanylate-Binding Proteins in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 7;26(12):5477. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125477. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA hypo-methylation and expression of GBP4 induces T cell exhaustion in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Aug 7;73(10):208. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03786-3. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39110249 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

