Spatial Differences and Influential Factors of Urban Carbon Emissions in China under the Target of Carbon Neutrality
- PMID: 35682024
- PMCID: PMC9180286
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19116427
Spatial Differences and Influential Factors of Urban Carbon Emissions in China under the Target of Carbon Neutrality
Abstract
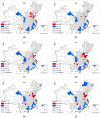
Cities are areas featuring a concentrated population and economy and are major sources of carbon emissions (CEs). The spatial differences and influential factors of urban carbon emissions (UCEs) need to be examined to reduce CEs and achieve the target of carbon neutrality. This paper selected 264 cities at the prefecture level in China from 2008 to 2018 as research objects. Their UCEs were calculated by the CE coefficient, and the spatial differences in them were analyzed using exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA). The influential factors of UCEs were studied with Geodetector. The results are as follows: (1) The UCEs were increasing gradually. Cities with the highest CEs over the study period were located in the urban agglomerations of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, middle reaches of the Yangtze River, and Chengdu-Chongqing. (2) The UCEs exhibited certain global and local spatial autocorrelations. (3) The industrial structure was the dominant factor influencing UCEs.
Keywords: Geodetector; carbon neutrality; exploratory spatial data analysis; influential factors; spatial differences; urban carbon emissions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mohmmed A., Li Z., Arowolo A.O., Su H., Deng X., Najmuddin O., Zhang Y. Driving factors of CO2 emissions and nexus with economic growth, development and human health in the Top Ten emitting countries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019;148:157–169. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.048. - DOI
-
- Marra A., Colantonio E. The path to renewable energy consumption in the European Union through drivers and barriers: A panel vector autoregressive approach. Socio Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020;76:100958. doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2020.100958. - DOI
-
- Zhang F., Jin G., Li J., Wang C., Xu N. Study on Dynamic Total Factor Carbon Emission Efficiency in China’s Urban Agglomerations. Sustainability. 2020;12:2675. doi: 10.3390/su12072675. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

