The Challenges and Strategies towards Healthy Eating during COVID-19 Home Confinement Period among Working Adults with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 Enrolled in a Weight Loss Program: Qualitative Findings
- PMID: 35682248
- PMCID: PMC9180068
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19116656
The Challenges and Strategies towards Healthy Eating during COVID-19 Home Confinement Period among Working Adults with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 Enrolled in a Weight Loss Program: Qualitative Findings
Abstract
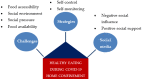
The COVID-19 pandemic has been affecting our lifestyles, such as work, living, and health. In Malaysia, the Restriction of Movement Order (RMO) was first announced in March 2020 to curb the spread of the virus. Since then, many Malaysians have been confined to their own home. This new lifestyle can cause a change of eating habits where healthy eating may be a challenge. Hence, our qualitative study explored the challenges and strategies for healthy eating during the first wave of the COVID-19 home confinement period among working adults overweight and obese in Malaysia. Eleven participants were individually interviewed through phone calls. The interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and then coded with NVIVO 12 based on thematic analysis. We found that social pressure, changes in the social setting, more free time to access food, and extra stock of unhealthy foods at home were among the challenges to healthy eating. Some participants countered these perceived challenges by reducing unhealthy food stock, limiting kitchen visits, and utilizing self-monitoring apps to monitor their calorie intake. Social media was not consistently perceived to influence their eating behavior during this period. We conclude that COVID-19 home confinement has created challenges to healthy eating habits among overweight and obese adults with overweight and obesity. Our study provides evidence that vulnerable groups such as overweight and obese individuals require specific nutritional support during pandemic-related confinement to enhance eating self-efficacy.
Keywords: COVID-19 home confinement; Social Cognitive Theory; challenges; healthy eating; strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Lee S.M., Yeong P.J., Ng K.Y. Movement Control Measures against COVID-19: Mobility Changes in Penang and Malaysia. 2020. [(accessed on 17 August 2021)]. Available online: https://penanginstitute.org/publications/monographs/movement-control-mea...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical