Quality of Informed Consent in Mammography Screening-The Polish Experience
- PMID: 35682316
- PMCID: PMC9180228
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19116735
Quality of Informed Consent in Mammography Screening-The Polish Experience
Abstract
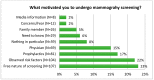
Breast cancer is one of the leading forms of cancers in women worldwide. In Poland, it accounts for approx. 20% of all cancers diagnosed, with approximately 11,000 new cases and 5000 deaths from this disease annually. To prevent unfavourable statistics, Poland introduced free breast cancer screening programmes, available to women aged 50-69. Over a million women take advantage of this programme each year. The aim of the research was to assess the quality of consent women give prior to mammography screening and address the question of whether this quality is sufficient to make an informed choice. The study was conducted on a representative group of 600 Polish women over 50 years old (475 of them had undergone mammography screening), who agreed to take part in the study. Using the computer-assisted interview technology (CATI) method, all women were asked about their perception of breast cancer and screening and those who had undergone mammography were quizzed about the consent process. They will form the focus of this research. The validated tool contained items on both the benefits and risks of screening. The results indicate that the quality of informed consent was insufficient. A discrepancy was observed in the awareness between the benefits and risks of mammography screening. The main motivations to undergo screening were: prophylactic purposes and the free-of-charge nature of this health service. Population-based screening programmes for breast cancer should be reconsidered in terms of information policy, and the quality of informed consent should be increased.
Keywords: benefit–risk ratio; breast cancer screening; mammography; quality of informed consent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Tailored Breast Screening Trial (TBST)].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Jul-Oct;37(4-5):317-27. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 24293498 Clinical Trial. Italian.
-
Two-view digital breast tomosynthesis versus digital mammography in a population-based breast cancer screening programme (To-Be): a randomised, controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jun;20(6):795-805. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30161-5. Epub 2019 May 8. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31078459 Clinical Trial.
-
One-view breast tomosynthesis versus two-view mammography in the Malmö Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Trial (MBTST): a prospective, population-based, diagnostic accuracy study.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Nov;19(11):1493-1503. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30521-7. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30322817 Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic assessment of benefits and risks to guide breast cancer screening decisions.JAMA. 2014 Apr 2;311(13):1327-35. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.1398. JAMA. 2014. PMID: 24691608 Review.
-
Preventive health care, 2001 update: screening mammography among women aged 40-49 years at average risk of breast cancer.CMAJ. 2001 Feb 20;164(4):469-76. CMAJ. 2001. PMID: 11233866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gajewski P., Szczeklik A. Interna Szczeklika Podręcznik Chorób Wewnętrznych. Medycyna Praktyczna; Kraków, Poland: 2017. Wyd. 8.
-
- Ministerstwo Zdrowia Program Profilaktyki Raka Piersi. [(accessed on 1 February 2021)]; Available online: Https://www.gov.pl/web/zdrowie/program-profilaktyki-raka-piersi-mammografia.
-
- Data on the Prophylactic Programmes Fulfilment, Made Available by the National Health Fund. [(accessed on 4 March 2021)]; Available online: Https://www.nfz.gov.pl/dla-pacjenta/programy-profilaktyczne/dane-o-reali...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical