Deep Brain Stimulation of the Medial Septal Area Can Modulate Gene Expression in the Hippocampus of Rats under Urethane Anesthesia
- PMID: 35682713
- PMCID: PMC9181580
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116034
Deep Brain Stimulation of the Medial Septal Area Can Modulate Gene Expression in the Hippocampus of Rats under Urethane Anesthesia
Abstract
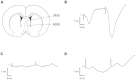
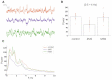
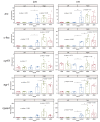
We studied the effects of stimulation of the medial septal area on the gene expression in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus. Rats under urethane anesthesia were implanted with a recording electrode in the right hippocampus and stimulating electrode in the dorsal medial septum (dMS) or medial septal nucleus (MSN). After one-hour-long deep brain stimulation, we collected ipsi- and contralateral dorsal and ventral hippocampi. Quantitative PCR showed that deep brain stimulation did not cause any changes in the intact contralateral dorsal and ventral hippocampi. A comparison of ipsi- and contralateral hippocampi in the control unstimulated animals showed that electrode implantation in the ipsilateral dorsal hippocampus led to a dramatic increase in the expression of immediate early genes (c-fos, arc, egr1, npas4), neurotrophins (ngf, bdnf) and inflammatory cytokines (il1b and tnf, but not il6) not only in the area close to implantation site but also in the ventral hippocampus. Moreover, the stimulation of MSN but not dMS further increased the expression of c-fos, egr1, npas4, bdnf, and tnf in the ipsilateral ventral but not dorsal hippocampus. Our data suggest that the activation of medial septal nucleus can change the gene expression in ventral hippocampal cells after their priming by other stimuli.
Keywords: bdnf; deep brain stimulation; dorsal hippocampus; early genes; inflammation; ngf; septum; ventral hippocampus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Induction of Long-Term Potentiation by Medial Septum Activation under Urethane Anesthesia Can Alter Gene Expression in the Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 19;24(16):12970. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612970. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629149 Free PMC article.
-
c-FOS expression after hippocampal deep brain stimulation in normal rats.Neuromodulation. 2014 Apr;17(3):213-7; discussion 216-7. doi: 10.1111/ner.12122. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Neuromodulation. 2014. PMID: 24118230
-
Expression of c-fos protein in rat brain elicited by electrical stimulation of the pontine parabrachial nucleus.J Neurosci. 1992 Sep;12(9):3582-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-09-03582.1992. J Neurosci. 1992. PMID: 1527597 Free PMC article.
-
The behavioral phenotype of pituitary adenylate-cyclase activating polypeptide-deficient mice in anxiety and depression tests is accompanied by blunted c-Fos expression in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, central projecting Edinger-Westphal nucleus, ventral lateral septum, and dorsal raphe nucleus.Neuroscience. 2012 Jan 27;202:283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.11.046. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22178610
-
Induction of hippocampal theta rhythm by electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area and its loss after septum inactivation.Brain Res. 2012 Feb 3;1436:51-67. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.12.003. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22221734
Cited by
-
The Induction of Long-Term Potentiation by Medial Septum Activation under Urethane Anesthesia Can Alter Gene Expression in the Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 19;24(16):12970. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612970. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629149 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

