Expression Profiles of Circulating MicroRNAs in XELOX-Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 35682716
- PMCID: PMC9180980
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116041
Expression Profiles of Circulating MicroRNAs in XELOX-Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer
Abstract
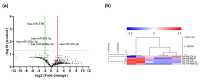
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common cancers and a leading cause of cancer deaths around the world. Chemotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for cancer patients, and has remarkably enhanced survival rates. However, it has many side effects. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs) have been intensively studied as potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and treatment monitoring. However, definitive biomarkers in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) are still lacking. The aim of this study was to identify the factors significant for neurological adverse events in GC patients receiving XELOX (oxaliplatin and capecitabine) chemotherapy. The results show that XELOX chemotherapy induces changes in the expression of hsa-miR-200c-3p, hsa-miR-885-5p, and hsa-miR-378f. Validation by qRT-PCR demonstrated that hsa-miR-378f was significantly downregulated in CIPN. Hsa-miR-378f was identified as showing a statistically significant correlation in GC patients receiving XELOX chemotherapy according to the analysis of differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs. Furthermore, 34 potential target genes were predicted using a web-based database for miRNA target prognostication and functional annotations. The identified genes are related to the peptidyl-serine phosphorylation and regulation of alternative mRNA splicing with enrichment in the gastric cancer, neurotrophin, MAPK, and AMPK signaling pathways. Collectively, these results provide information useful for developing promising strategies for the treatment of XELOX-chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; gastric cancer; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

