Muscle Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mechanism and Clinical Implications-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35682722
- PMCID: PMC9181340
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116047
Muscle Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mechanism and Clinical Implications-A Narrative Review
Abstract
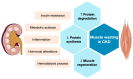
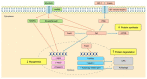
Muscle wasting, known to develop in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), is a deleterious consequence of numerous complications associated with deteriorated renal function. Muscle wasting in CKD mainly involves dysregulated muscle protein metabolism and impaired muscle cell regeneration. In this narrative review, we discuss the cardinal role of the insulin-like growth factor 1 and myostatin signaling pathways, which have been extensively investigated using animal and human studies, as well as the emerging concepts in microRNA- and gut microbiota-mediated regulation of muscle mass and myogenesis. To ameliorate muscle loss, therapeutic strategies, including nutritional support, exercise programs, pharmacological interventions, and physical modalities, are being increasingly developed based on advances in understanding its underlying pathophysiology.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; exercise; molecular mechanism; muscle regeneration; muscle wasting; nutrition; pharmaceutical intervention; physical modality; protein metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Skeletal muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease: the emerging role of microRNAs.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020 Sep 1;35(9):1469-1478. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfz193. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020. PMID: 31603229 Review.
-
Mechanisms of muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014 Sep;10(9):504-16. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.112. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24981816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of muscle wasting by the plant-derived compound ursolic acid in a model of chronic kidney disease.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017 Apr;8(2):327-341. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12162. Epub 2016 Nov 17. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017. PMID: 27897418 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-cachectic factors link experimental and human chronic kidney disease to skeletal muscle wasting programs.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jun 1;131(11):e135821. doi: 10.1172/JCI135821. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34060483 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: a new therapeutic frontier for muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease.Kidney Int. 2012 Aug;82(4):373-4. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.150. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22846810
Cited by
-
Diet Supplementation with Ketoanalogues, Inulin, and Calcium Citrate in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 10;14(12):1638. doi: 10.3390/life14121638. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768345 Free PMC article.
-
Uremic Myopathy and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13515. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113515. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362298 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Linking Chronic Kidney Disease and Sarcopenia in Aging: An Integrated Perspective.Clin Interv Aging. 2025 Apr 8;20:449-458. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S516704. eCollection 2025. Clin Interv Aging. 2025. PMID: 40226833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of the Nutrition-Inflammation Status on the Functionality of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 10;14(22):4745. doi: 10.3390/nu14224745. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432432 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and molecular mechanism of muscle wasting in end stage renal disease.BMB Rep. 2023 Aug;56(8):426-438. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0097. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 37482754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kirkman D.L., Bohmke N., Carbone S., Garten R.S., Rodriguez-Miguelez P., Franco R.L., Kidd J.M., Abbate A. Exercise intolerance in kidney diseases: Physiological contributors and therapeutic strategies. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021;320:F161–F173. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00437.2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

