Connective Tissue Growth Factor in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Breaking the Bridge
- PMID: 35682743
- PMCID: PMC9181498
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116064
Connective Tissue Growth Factor in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Breaking the Bridge
Abstract
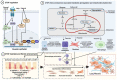
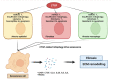
CTGF is upregulated in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), characterized by the deposition of a pathological extracellular matrix (ECM). Additionally, many omics studies confirmed that aberrant cellular senescence-associated mitochondria dysfunction and metabolic reprogramming had been identified in different IPF lung cells (alveolar epithelial cells, alveolar endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages). Here, we reviewed the role of the CTGF in IPF lung cells to mediate anomalous senescence-related metabolic mechanisms that support the fibrotic environment in IPF.
Keywords: CTGF; chronic respiratory diseases; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; metabolic dysregulation; mitochondria dysfunction; pro-fibrotic; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Cellular Senescence Is Independent from Profibrotic Fibroblast-Deposited ECM.Cells. 2021 Jun 29;10(7):1628. doi: 10.3390/cells10071628. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34209854 Free PMC article.
-
CCN5 overexpression inhibits profibrotic phenotypes via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in lung fibroblasts isolated from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in an in vivo model of lung fibrosis.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Feb;33(2):478-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1565. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24276150
-
Connective-Tissue Growth Factor Contributes to TGF-β1-induced Lung Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Mar;66(3):260-270. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0504OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34797990
-
Mitochondria dysfunction and metabolic reprogramming as drivers of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Redox Biol. 2020 Jun;33:101509. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101509. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32234292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular metabolomics of pulmonary fibrosis, from amino acids to lipids.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):C689-C695. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00586.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33471621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in understanding and treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent insights and emerging therapies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 7;14:1205948. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1205948. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37608885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 expression is not associated with an activated fibroblast phenotype in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 31;13:953771. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.953771. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120350 Free PMC article.
-
Trials and Treatments: An Update on Pharmacotherapy for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;13(2):486. doi: 10.3390/life13020486. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Function Changes and Connective Tissue Growth Factor Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Other Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases, and Post-COVID Fibrosis.Cureus. 2025 Jul 24;17(7):e88645. doi: 10.7759/cureus.88645. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40717875 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Targets to Reduce Excessive Scarring in Response to Tissue Injury.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 27;13(5):758. doi: 10.3390/biom13050758. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rendin L.E., Löfdahl A., Xiong L., Michaliková B., Zhou X., Dellgren G., Westergren-Thorsson G. Altered ECM niche in IPF affect structural remodeling. Eur. Respir. J. 2020;56:3376.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

