Connective Tissue Growth Factor in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Breaking the Bridge
- PMID: 35682743
- PMCID: PMC9181498
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116064
Connective Tissue Growth Factor in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Breaking the Bridge
Abstract
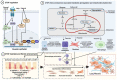
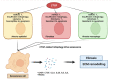
CTGF is upregulated in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), characterized by the deposition of a pathological extracellular matrix (ECM). Additionally, many omics studies confirmed that aberrant cellular senescence-associated mitochondria dysfunction and metabolic reprogramming had been identified in different IPF lung cells (alveolar epithelial cells, alveolar endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages). Here, we reviewed the role of the CTGF in IPF lung cells to mediate anomalous senescence-related metabolic mechanisms that support the fibrotic environment in IPF.
Keywords: CTGF; chronic respiratory diseases; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; metabolic dysregulation; mitochondria dysfunction; pro-fibrotic; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rendin L.E., Löfdahl A., Xiong L., Michaliková B., Zhou X., Dellgren G., Westergren-Thorsson G. Altered ECM niche in IPF affect structural remodeling. Eur. Respir. J. 2020;56:3376.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

