Chemogenetic Activation of Astrocytes in the Basolateral Amygdala Contributes to Fear Memory Formation by Modulating the Amygdala-Prefrontal Cortex Communication
- PMID: 35682767
- PMCID: PMC9181030
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116092
Chemogenetic Activation of Astrocytes in the Basolateral Amygdala Contributes to Fear Memory Formation by Modulating the Amygdala-Prefrontal Cortex Communication
Abstract
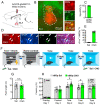
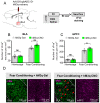
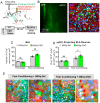
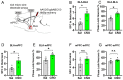
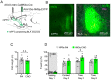
The basolateral amygdala (BLA) is one of the key brain areas involved in aversive learning, especially fear memory formation. Studies of aversive learning in the BLA have largely focused on neuronal function, while the role of BLA astrocytes in aversive learning remains largely unknown. In this study, we manipulated the BLA astrocytes by expressing the Gq-coupled receptor hM3q and discovered that astrocytic Gq modulation during fear conditioning promoted auditorily cued fear memory but did not affect less stressful memory tasks or induce anxiety-like behavior. Moreover, chemogenetic activation of BLA astrocytes during memory retrieval had no effect on fear memory expression. In addition, astrocytic Gq activation increased c-Fos expression in the BLA and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) during fear conditioning, but not in the home cage. Combining these results with retrograde virus tracing, we found that the activity of mPFC-projecting BLA neurons showed significant enhancement after astrocytic Gq activation during fear conditioning. Electrophysiology recordings showed that activating astrocytic Gq in the BLA promoted spike-field coherence and phase locking percentage, not only within the BLA but also between the BLA and the mPFC. Finally, direct chemogenetic activation of mPFC-projecting BLA neurons during fear conditioning enhanced cued fear memory. Taken together, our data suggest that astrocytes in the BLA may contribute to aversive learning by modulating amygdala-mPFC communication.
Keywords: anxiety; astrocytes; basolateral amygdala; chemogenetic; electrophysiology; fear conditioning; medial prefrontal cortex; neurons; projection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aggleton J.P. The Amygdala: A Functional Analysis. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2000.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 11103721/General Research Fund, Research Grants Council of Hong Kong
- 11102820/General Research Fund, Research Grants Council of Hong Kong
- 11100018/General Research Fund, Research Grants Council of Hong Kong
- 3171101014, N_CityU114/17/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and RGC Joint Research Scheme
- CityU 9445909/Innovation and Technology Fund Hong Kong
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

