Lupeol Treatment Attenuates Activation of Glial Cells and Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Neuropathology in Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury
- PMID: 35682768
- PMCID: PMC9181489
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116086
Lupeol Treatment Attenuates Activation of Glial Cells and Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Neuropathology in Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
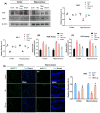
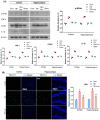
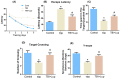
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) signifies a major cause of death and disability. TBI causes central nervous system (CNS) damage under a variety of mechanisms, including protein aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation. Astrocytes and microglia, cells of the CNS, are considered the key players in initiating an inflammatory response after injury. Several evidence suggests that activation of astrocytes/microglia and ROS/LPO have the potential to cause more harmful effects in the pathological processes following traumatic brain injury (TBI). Previous studies have established that lupeol provides neuroprotection through modulation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in Aβ and LPS model and neurodegenerative disease. However, the effects of lupeol on apoptosis caused by inflammation and oxidative stress in TBI have not yet been investigated. Therefore, we explored the role of Lupeol on antiapoptosis, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidative stress and its potential mechanism following TBI. In these experiments, adult male mice were randomly divided into four groups: control, TBI, TBI+ Lupeol, and Sham group. Western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, and ROS/LPO assays were performed to investigate the role of lupeol against neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Lupeol treatment reversed TBI-induced behavioral and memory disturbances. Lupeol attenuated TBI-induced generation of reactive oxygen species/lipid per oxidation (ROS/LPO) and improved the antioxidant protein level, such as nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme-oxygenase 1 (HO-1) in the mouse brain. Similarly, our results indicated that lupeol treatment inhibited glial cell activation, p-NF-κB, and downstream signaling molecules, such as TNF-α, COX-2, and IL-1β, in the mouse cortex and hippocampus. Moreover, lupeol treatment also inhibited mitochondrial apoptotic signaling molecules, such as caspase-3, Bax, cytochrome-C, and reversed deregulated Bcl2 in TBI-treated mice. Overall, our study demonstrated that lupeol inhibits the activation of astrocytes/microglia and ROS/LPO that lead to oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis followed by TBI.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; glia activation; lupeol; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Aucubin alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation via Nrf2-mediated signaling activity in experimental traumatic brain injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jun 15;17(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01863-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32539839 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic brain injury-induced downregulation of Nrf2 activates inflammatory response and apoptotic cell death.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Dec;97(12):1627-1641. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01851-4. Epub 2019 Nov 22. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31758217
-
N-acetylcysteine amide provides neuroprotection via Nrf2-ARE pathway in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Dec 4;12:4117-4127. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S179227. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30584276 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Nrf2-Mediated Oxidative Stress Response in Traumatic Brain Injury: Therapeutic Perspectives of Phytochemicals.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 4;2022:1015791. doi: 10.1155/2022/1015791. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35419162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the NF-E2-Related Factor 2 Pathway: a Novel Strategy for Traumatic Brain Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Feb;55(2):1773-1785. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0456-z. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28224478 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Neuroprotective Potential of Sacred Ficus Trees.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 9;14(22):4731. doi: 10.3390/nu14224731. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupeol protect against LPS-induced neuroinflammation and amyloid beta in adult mouse hippocampus.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 10;11:1414696. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1414696. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39050141 Free PMC article.
-
IFI204 in microglia mediates traumatic brain injury-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and pyroptosis via SENP7 interaction.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 May 23;41(1):89. doi: 10.1007/s10565-025-10032-8. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40407969 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of aging and oxidative stress in metabolic and nervous system disorders: programmed cell death and molecular signal transduction crosstalk.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 8;14:1273570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273570. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial effect of lupeol and metformin in mouse model of intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced dementia.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Jun;39(5):661-678. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01364-1. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 38842663
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

