New Developments in Carbonic Anhydrase IX-Targeted Fluorescence and Nuclear Imaging Agents
- PMID: 35682802
- PMCID: PMC9181387
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116125
New Developments in Carbonic Anhydrase IX-Targeted Fluorescence and Nuclear Imaging Agents
Abstract
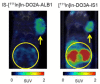
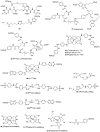
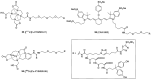
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is a tumor-specific and hypoxia-induced biomarker for the molecular imaging of solid malignancies. The nuclear- and optical-imaging of CAIX-expressing tumors have received great attention due to their potential for clinical applications. Nuclear imaging is a powerful tool for the non-invasive diagnosis of primary and metastatic CAIX-positive tumors and for the assessment of responses to antineoplastic treatment. Intraoperative optical fluorescence imaging provides improved visualization for surgeons to increase the discrimination of tumor lesions, allowing for safer surgical treatment. Over the past decades, many CAIX-targeted molecular imaging probes, based on monoclonal antibodies, antibody fragments, peptides, and small molecules, have been reported. In this review, we outline the recent development of CAIX-targeted probes for single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), and near-infrared fluorescence imaging (NIRF), and we discuss issues yet to be addressed.
Keywords: PET; SPECT; cancer; carbonic anhydrase IX; fluorescence imaging; imaging agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



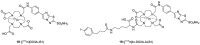

Similar articles
-
Investigation of hypoxia and carbonic anhydrase IX expression in a renal cell carcinoma xenograft model with oxygen tension measurements and ¹²⁴I-cG250 PET/CT.Urol Oncol. 2011 Jul-Aug;29(4):411-20. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.03.028. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Urol Oncol. 2011. PMID: 19523858
-
Optical Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma with Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase IX Monoclonal Antibody Girentuximab.J Nucl Med. 2014 Jun;55(6):1035-40. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.137356. Epub 2014 Apr 21. J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 24752673
-
Targeting CAIX with [64Cu]XYIMSR-06 Small Molecular Radiotracer Enables Noninvasive PET Imaging of Malignant Glioma in U87 MG Tumor Cell Xenograft Mice.Mol Pharm. 2019 Apr 1;16(4):1532-1540. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b01210. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30803240
-
Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX with small organic ligands.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015 Jun;26:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25721398 Review.
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) as a mediator of hypoxia-induced stress response in cancer cells.Subcell Biochem. 2014;75:255-69. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7359-2_13. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24146383 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor perfusion enhancement by microbubbles ultrasonic cavitation reduces tumor glycolysis metabolism and alleviate tumor acidosis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 18;14:1424824. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1424824. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39091919 Free PMC article.
-
High-Affinity NIR-Fluorescent Inhibitors for Tumor Imaging via Carbonic Anhydrase IX.Bioconjug Chem. 2024 Jun 19;35(6):790-803. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.4c00144. Epub 2024 May 15. Bioconjug Chem. 2024. PMID: 38750635 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging hypoxia for head and neck cancer: current status, challenges, and prospects.Theranostics. 2025 Jul 11;15(16):8012-8030. doi: 10.7150/thno.112781. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40860130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies for Targeted Fluorescence-Guided Surgery: A Review of Applicability across Multiple Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 4;16(5):1045. doi: 10.3390/cancers16051045. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular imaging of renal cell carcinomas: ready for prime time.Nat Rev Urol. 2025 Jun;22(6):336-353. doi: 10.1038/s41585-024-00962-z. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Nat Rev Urol. 2025. PMID: 39543358 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

